The mechanisms of action of metformin
- PMID: 28776086
- PMCID: PMC5552828
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-017-4342-z
The mechanisms of action of metformin
Abstract
Metformin is a widely-used drug that results in clear benefits in relation to glucose metabolism and diabetes-related complications. The mechanisms underlying these benefits are complex and still not fully understood. Physiologically, metformin has been shown to reduce hepatic glucose production, yet not all of its effects can be explained by this mechanism and there is increasing evidence of a key role for the gut. At the molecular level the findings vary depending on the doses of metformin used and duration of treatment, with clear differences between acute and chronic administration. Metformin has been shown to act via both AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-dependent and AMPK-independent mechanisms; by inhibition of mitochondrial respiration but also perhaps by inhibition of mitochondrial glycerophosphate dehydrogenase, and a mechanism involving the lysosome. In the last 10 years, we have moved from a simple picture, that metformin improves glycaemia by acting on the liver via AMPK activation, to a much more complex picture reflecting its multiple modes of action. More work is required to truly understand how this drug works in its target population: individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: AMPK; Biguanide; Diabetes; Metformin; Review.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding
ERP holds a Wellcome Trust Investigator award (102820/Z/13/Z). DGH holds a Wellcome Trust Investigator award (204766/Z/16/Z) and a Cancer Research UK Programme Grant (C37030/A15101). GR acknowledges current funding from the Cunningham Trust.
Duality of interest
The authors declare that there is no duality of interest associated with this manuscript.
Contribution statement
All authors were responsible for drafting the article and revising it critically for important intellectual content. All authors approved the version to be published.
Figures

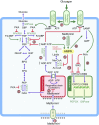

References
-
- Howlett HCS, Bailey CJ. Galegine and antidiabetic plants. In: Bailey CJ, Campbell IW, Chan JCN, Davidson JA, Howlett HCS, Ritz P, editors. Metformin—the gold standard. Chichester: Wiley; 2007. pp. 3–9.
-
- Muller H, Reinwein H. Zur pharmakologie des Galegins. Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1927;125:212–228. doi: 10.1007/BF01862957. - DOI
-
- Howlett HCS, Bailey CJ. Discovery of metformin. In: Bailey CJ, Campbell IW, Chan JCN, Davidson JA, Howlett HCS, Ritz P, editors. Metformin—the gold standard. Chichester: Wiley; 2007. pp. 11–16.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

