Regulator of G protein signaling 14 (RGS14) is expressed pre- and postsynaptically in neurons of hippocampus, basal ganglia, and amygdala of monkey and human brain
- PMID: 28776200
- PMCID: PMC5951638
- DOI: 10.1007/s00429-017-1487-y
Regulator of G protein signaling 14 (RGS14) is expressed pre- and postsynaptically in neurons of hippocampus, basal ganglia, and amygdala of monkey and human brain
Abstract
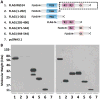
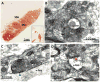
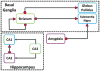
Regulator of G protein signaling 14 (RGS14) is a multifunctional signaling protein primarily expressed in mouse pyramidal neurons of hippocampal area CA2 where it regulates synaptic plasticity important for learning and memory. However, very little is known about RGS14 protein expression in the primate brain. Here, we validate the specificity of a new polyclonal RGS14 antibody that recognizes not only full-length RGS14 protein in primate, but also lower molecular weight forms of RGS14 protein matching previously predicted human splice variants. These putative RGS14 variants along with full-length RGS14 are expressed in the primate striatum. By contrast, only full-length RGS14 is expressed in hippocampus, and shorter variants are completely absent in rodent brain. We report that RGS14 protein immunoreactivity is found both pre- and postsynaptically in multiple neuron populations throughout hippocampal area CA1 and CA2, caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus, substantia nigra, and amygdala in adult rhesus monkeys. A similar cellular expression pattern of RGS14 in the monkey striatum and hippocampus was further confirmed in humans. Our electron microscopy data show for the first time that RGS14 immunostaining localizes within nuclei of striatal neurons in monkeys. Taken together, these findings suggest new pre- and postsynaptic regulatory functions of RGS14 and RGS14 variants, specific to the primate brain, and provide evidence for unconventional roles of RGS14 in the nuclei of striatal neurons potentially important for human neurophysiology and disease.
Keywords: Amygdala; Basal ganglia; Hippocampus; Human; Nucleus; RGS14.
Figures











References
-
- Albin RL, Young AB, Penney JB. The functional anatomy of basal ganglia disorders. Trends Neurosci. 1989;12:366–375. - PubMed
-
- Amstadter AB, Koenen KC, Ruggiero KJ, Acierno R, Galea S, Kilpatrick DG, Gelernter J. Variation in RGS2 is associated with suicidal ideation in an epidemiological study of adults exposed to the 2004 Florida hurricanes. Arch Suicide Res. 2009b;13:349–357. doi: 10.1080/13811110903266541. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 GM008602/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS074975/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P51 OD011132/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P51OD011132/National Institutes of Health
- F31 NS098648/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG025688/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS087488/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F31NS098648/National Institutes of Health
- R01 NS037112/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008602/National Institutes of Health
- 5R01NS037112/National Institutes of Health
- 1R21 NS087488/National Institutes of Health
- P30 NS055077/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

