Diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease in the Eastern Mediterranean Region: findings from the Global Burden of Disease 2015 study
- PMID: 28776240
- PMCID: PMC5973961
- DOI: 10.1007/s00038-017-1014-1
Diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease in the Eastern Mediterranean Region: findings from the Global Burden of Disease 2015 study
Abstract
Objectives: We used findings from the Global Burden of Disease 2015 study to update our previous publication on the burden of diabetes and chronic kidney disease due to diabetes (CKD-DM) during 1990-2015.
Methods: We extracted GBD 2015 estimates for prevalence, mortality, and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) of diabetes (including burden of low vision due to diabetes, neuropathy, and amputations and CKD-DM for 22 countries of the EMR from the GBD visualization tools.
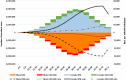
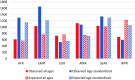
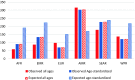
Results: In 2015, 135,230 (95% UI 123,034-148,184) individuals died from diabetes and 16,470 (95% UI 13,977-18,961) from CKD-DM, 216 and 179% increases, respectively, compared to 1990. The total number of people with diabetes was 42.3 million (95% UI 38.6-46.4 million) in 2015. DALY rates of diabetes in 2015 were significantly higher than the expected rates based on Socio-demographic Index (SDI).
Conclusions: Our study showed a large and increasing burden of diabetes in the region. There is an urgency in dealing with diabetes and its consequences, and these efforts should be at the forefront of health prevention and promotion.
Keywords: Burden of disease; Chronic kidney disease; Diabetes; Eastern Mediterranean Region.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this paper have complied with all ethical standards and do not have any conflicts of interest to disclose at the time of submission. The funding source played no role in the design of the study, the analysis and interpretation of data, and the writing of the paper.
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest at this time.
Figures

References
-
- Afshin A, Micha R, Khatibzadeh S, et al. The impact of dietary habits and metabolic risk factors on cardiovascular and diabetes mortality in countries of the Middle East and North Africa in 2010: a comparative risk assessment analysis. BMJ Open. 2015;5(5):e006385. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-006385. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brunton SA, Polonsky WH. Hot topics in primary care: medication adherence in type 2 diabetes mellitus: real-world strategies for addressing a common problem. J Fam Pract. 2017;66(4 Suppl):S46–S51. - PubMed
-
- Davies MJ, Gray LJ, Troughton J, et al. A community-based primary prevention programme for type 2 diabetes mellitus integrating identification and lifestyle intervention for prevention: a cluster randomised controlled trial. Southampton (UK): Programme Grants for Applied Research; 2017. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

