Risk of Stroke in Elderly Dialysis Patients
- PMID: 28776341
- PMCID: PMC5546965
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.9.1460
Risk of Stroke in Elderly Dialysis Patients
Abstract
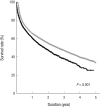
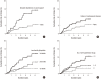
Despite the current knowledge about the risk of stroke and its related factors in general population, this issue in elderly patients receiving dialysis remains unresolved. Firstly, to compare the risk of stroke between hemodialysis (HD) and peritoneal dialysis (PD), data on 13,065 incident dialysis patients (aged ≥ 65 years; 10,675 in HD and 2,390 in PD) were retrieved from the Korean Health Insurance dataset. Secondly, to identify the risk factors of stroke amongst various clinical and laboratory parameters in HD, 980 elderly patients were retrospectively analyzed using an independent prospective cohort from 31 dialysis centers. For a mean duration of 1.8 years (maximum of 5 years), the risk of all cardiovascular diseases (ischemic heart disease and stroke) did not differ between HD and PD. However, when analyses were conducted separately by subtype, the risk of stroke, not ischemic heart disease, was significantly higher in HD patients than in PD patients. When the risk factors of stroke were probed after HD for a mean duration of 2.6 years (maximum of 7 years), the absolute dependence on social support, a previous history of cardiovascular disease, high levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and the use of a high number of anti-hypertensive drugs were identified as being significant. Based on the discrepancy of stroke risk between modalities and the HD-tailored risk factors of stroke, the monitoring and management of these factors may be a key strategy to reduce the risk of stroke in elderly patients receiving dialysis.
Keywords: Aged; Cardiovascular Diseases; Kidney Failure, Chronic; Renal Dialysis; Stroke.
© 2017 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
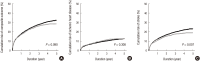
Comment in
-
Stroke in Korean Dialysis Population: Another Health Threat Never to Be Underestimated.J Korean Med Sci. 2017 Sep;32(9):1383-1384. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.9.1383. J Korean Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28776331 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Brønnum-Hansen H, Davidsen M, Thorvaldsen P, Danish MONICA Study Group Long-term survival and causes of death after stroke. Stroke. 2001;32(9):2131–2136. - PubMed
-
- Di Carlo A. Human and economic burden of stroke. Age Ageing. 2009;38:4–5. - PubMed
-
- Redón J, Cea-Calvo L, Lozano JV, Martí-Canales JC, Llisterri JL, Aznar J, González-Esteban J. Investigators of the PREV-ICTUS study. Blood pressure and estimated risk of stroke in the elderly population of Spain: the PREV-ICTUS study. Stroke. 2007;38:1167–1173. - PubMed
-
- Schiffrin EL, Lipman ML, Mann JF. Chronic kidney disease: effects on the cardiovascular system. Circulation. 2007;116:85–97. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

