Synthesis and Evaluation of Chloroquine-Containing DMAEMA Copolymers as Efficient Anti-miRNA Delivery Vectors with Improved Endosomal Escape and Antimigratory Activity in Cancer Cells
- PMID: 28776937
- PMCID: PMC5997184
- DOI: 10.1002/mabi.201700194
Synthesis and Evaluation of Chloroquine-Containing DMAEMA Copolymers as Efficient Anti-miRNA Delivery Vectors with Improved Endosomal Escape and Antimigratory Activity in Cancer Cells
Abstract
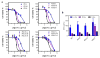
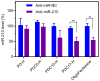
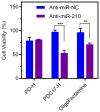
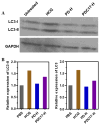
Chloroquine-containing 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate copolymers (PDCs) are synthesized by reversible addition-fragmentation chain-transfer polymerization. Systematic evaluation is performed to test the hypothesis that presence of chloroquine (CQ) in the PDC structure will improve miRNA delivery due to enhanced endosomal escape while simultaneously contribute to anticancer activity of PDC/miRNA polyplexes through inhibition of cancer cell migration. The results show that miRNA delivery efficiency is dependent both on the molecular weight and CQ. The best performing PDC/miRNA polyplexes show effective endosomal escape of miRNA. PDC polyplexes with therapeutic miR-210 show promising anticancer activity in human breast cancer cells. PDC/miRNA polyplexes show excellent ability to inhibit migration of cancer cells. Overall, this study supports the use of PDC as a promising polymeric drug platform for use in combination anti-metastatic and anticancer miRNA therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: chloroquine; endosomal escape; miRNA delivery; polymeric drug; polyplex.
© 2017 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

