Sink or Collaborate: How the Immersive Model Has Helped Address Typical Adolescent and Young Adult Barriers at a Single Institution and Kept the Adolescent and Young Adult Program Afloat
- PMID: 28777007
- PMCID: PMC5725631
- DOI: 10.1089/jayao.2017.0051
Sink or Collaborate: How the Immersive Model Has Helped Address Typical Adolescent and Young Adult Barriers at a Single Institution and Kept the Adolescent and Young Adult Program Afloat
Keywords: AYA oncology; AYA program; model; multidisciplinary collaboration; psychosocial.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
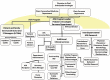
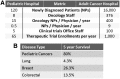


Similar articles
-
Adolescent and young adult oncology training for health professionals: a position statement.J Clin Oncol. 2010 Nov 10;28(32):4858-61. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.30.5508. Epub 2010 Sep 7. J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20823410
-
Children's Oncology Group's 2013 blueprint for research: adolescent and young adult oncology.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2013 Jun;60(6):1055-8. doi: 10.1002/pbc.24431. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23424167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Collaboration and Networking.Prog Tumor Res. 2016;43:50-63. doi: 10.1159/000447071. Epub 2016 Sep 5. Prog Tumor Res. 2016. PMID: 27595356 Review.
-
Family-Oriented Rehabilitation (FOR) and Rehabilitation of Adolescents and Young Adults (AYA) in Pediatric Oncology.Oncol Res Treat. 2017;40(12):752-758. doi: 10.1159/000484609. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Oncol Res Treat. 2017. PMID: 29151110 Review.
-
Starting an adolescent and young adult program: some success stories and some obstacles to overcome.J Clin Oncol. 2010 Nov 10;28(32):4850-7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.23.8097. Epub 2010 May 17. J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20479411
Cited by
-
Developing a Comprehensive Adolescent and Young Adult Cancer Program: Lessons Learned from 7 Years of Growth and Progress.J Adolesc Young Adult Oncol. 2023 Dec;12(6):868-878. doi: 10.1089/jayao.2023.0015. Epub 2023 May 4. J Adolesc Young Adult Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37155196 Free PMC article.
-
The Creation of a Comprehensive Adolescent and Young Adult Cancer Survivorship Program: "Lost in Transition" No More.J Adolesc Young Adult Oncol. 2021 Aug;10(4):397-403. doi: 10.1089/jayao.2020.0024. Epub 2020 Jul 8. J Adolesc Young Adult Oncol. 2021. PMID: 32640864 Free PMC article.
-
Higher than reported adolescent and young adult clinical trial enrollment during the "Golden Age" of melanoma clinical trials.Cancer Med. 2018 Apr;7(4):991-996. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1307. Epub 2018 Feb 25. Cancer Med. 2018. PMID: 29478277 Free PMC article.
-
Avoir sa santé en main : le sentiment d'habilitation tel que perçu par les jeunes adultes souffrant d'un cancer avancé.Can Oncol Nurs J. 2020 Apr 1;30(2):103-112. doi: 10.5737/23688076302103112. eCollection 2020 Spring. Can Oncol Nurs J. 2020. PMID: 33118994 Free PMC article.
-
Taking control over our health: Empowerment as perceived by young adults living with advanced cancer.Can Oncol Nurs J. 2020 Apr 1;30(2):93-102. doi: 10.5737/2368807630293102. eCollection 2020 Spring. Can Oncol Nurs J. 2020. PMID: 33118996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zebrack BJ, Block R, Hayes-Lattin B, et al. . Psychosocial service use and unmet need among recently diagnosed adolescent and young adult cancer patients. Cancer. 2013;119(1):201–4 - PubMed
-
- Murphy D, Klosky JL, Reed DR, et al. . The importance of assessing priorities of reproductive health concerns among adolescent and young adult patients with cancer. Cancer. 2015;121(15):2529–36 - PubMed
-
- Bleyer A, Montello M, Budd T, Saxman S. National survival trends of young adults with sarcoma: lack of progress is associated with lack of clinical trial participation. Cancer. 2005;103(9):1891–7 - PubMed
-
- Bleyer AW, Barr RD, Albritton KH, Phillips M, Siegel S. (Eds). Cancer in Adolescents and Young Adults. Berlin: Springer Verlag; 2007; pp. 83–98
-
- Isakoff MS, Freyer DR, Bleyer A. Young adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with a pediatric-inspired regimen do not need a bone marrow transplant in first remission. Blood. 2013;121(26):5253–5 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
