Unexpected metabolic function of a tRNA synthetase
- PMID: 28777042
- PMCID: PMC5788480
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1324127
Unexpected metabolic function of a tRNA synthetase
Keywords: EPRS; FATP1; GAIT; S6K1; adiposity; insulin; interferon-gamma; mTORC1; metabolism; tRNA synthetase.
Figures
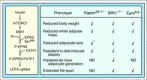
Comment on
-
EPRS is a critical mTORC1-S6K1 effector that influences adiposity in mice.Nature. 2017 Feb 16;542(7641):357-361. doi: 10.1038/nature21380. Epub 2017 Feb 8. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28178239 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arif A, Jia J, Mukhopadhyay R, Willard B, Kinter M, Fox PL. Two-site phosphorylation of EPRS coordinates multimodal regulation of noncanonical translational control activity. Mol Cell 2009; 35:164-80; PMID:19647514; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2009.05.028 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee EY, Lee HC, Kim HK, Jang SY, Park SJ, Kim YH, Kim JH, Hwang J, Kim JH, Kim TH, Arif A, Kim SY, Choi YK, Lee C, Lee CH, Jung JU, Fox PL, Kim S, Lee JS, Kim MH. Infection-specific phosphorylation of glutamyl-prolyl tRNA synthetase induces antiviral immunity. Nat Immunol 2016; 17:1252-62; PMID:27595231; https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.3542 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arif A, Terenzi F, Potdar AA, Jia J, Sacks J, China A, Halawani D, Vasu K, Li X, Brown JM, Chen J, Kozma SC, Thomas G, Fox PL. EPRS is a critical mTORC1-S6K1 effector that influences adiposity in mice. Nature 2017; 542:357-61; PMID:28178239; https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21380 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clemens MJ. Does protein phosphorylation play a role in translational control by eukaryotic aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases? Trends Biochem Sci 1990; 15:172-5; PMID:2193433; https://doi.org/10.1016/0968-0004(90)90153-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Selman C, Tullet JM, Wieser D, Irvine E, Lingard SJ, Choudhury AI, Claret M, Al-Qassab H, Carmignac D, Ramadani F, Woods A, Robinson IC, Schuster E, Batterham RL, Kozma SC, Thomas G, Carling D, Okkenhaug K, Thornton JM, Partridge L, Gems D, Withers DJ. Ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 signaling regulates mammalian life span. Science 2009; 326:140-4; PMID:19797661; https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1177221 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
