Gonorrhea and Chlamydia Case Detection Increased When Testing Increased in a Multisite US HIV Cohort, 2004-2014
- PMID: 28777262
- PMCID: PMC5680900
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000001514
Gonorrhea and Chlamydia Case Detection Increased When Testing Increased in a Multisite US HIV Cohort, 2004-2014
Abstract
Objectives: Annual screening for gonorrhea [Neisseria gonorrhoeae (NG)] and chlamydia [Chlamydia trachomatis (CT)] is recommended for all sexually active persons living with HIV but is poorly implemented. Studies demonstrating no increases in NG and/or CT (NG/CT) case detection in clinics that successfully expanded NG/CT screening raise questions about this broad screening approach. We evaluated NG/CT case detection in the HIV Research Network during 2004-2014, a period of expanding testing.
Methods: We analyzed linear time trends in annual testing (patients tested divided by all patients in care), test positivity (patients positive divided by all tested), and case detection (the number of patients with a positive result divided by all patients in care) using multivariate repeated measures logistic regression. We determined trends overall and stratified by men who have sex with men (MSM), men who have sex exclusively with women, and women.
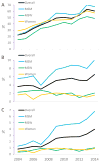
Results: Among 15,614 patients (50% MSM, 26% men who have sex exclusively with women, and 24% women), annual NG/CT testing increased from 22% in 2004 to 60% in 2014 [adjusted odds ratio (AOR) per year 1.22 (1.21-1.22)]. Despite the increase in testing, test positivity also increased [AOR per year 1.10 (1.07-1.12)], and overall case detection increased from 0.8% in 2004 to 3.9% in 2014 [AOR per year 1.20 (1.17-1.22)]. Case detection was highest among MSM but increased over time among all 3 groups.
Conclusions: NG/CT case detection increased as testing expanded in the population. This supports a broad approach to NG/CT screening among persons living with HIV to decrease transmission and complications of NG/CT and of HIV.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Soni S, White JA. Self-screening for Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis in the human immunodeficiency virus clinic—high yields and high acceptability. Sex Transm Dis. 2011;38(12):1107–1109. - PubMed
-
- Phipps W, Stanley H, Kohn R, Stansell J, Klausner JD. Syphilis, chlamydia, and gonorrhea screening in HIV-infected patients in primary care, San Francisco, California, 2003. AIDS Patient Care STDs. 2005;19(8):495–498. - PubMed
-
- Heiligenberg M, van der Loeff MFS, de Vries HJ, et al. Low prevalence of asymptomatic sexually transmitted infections in HIV-infected heterosexuals visiting an HIV clinic in the Netherlands. AIDS. 2012;26(5):646–649. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical