Unintentional Child and Adolescent Drowning Mortality from 2000 to 2013 in 21 Countries: Analysis of the WHO Mortality Database
- PMID: 28777318
- PMCID: PMC5580579
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph14080875
Unintentional Child and Adolescent Drowning Mortality from 2000 to 2013 in 21 Countries: Analysis of the WHO Mortality Database
Abstract
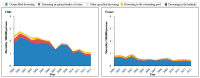
Limited research considers change over time for drowning mortality among individuals under 20 years of age, or the sub-cause (method) of those drownings. We assessed changes in under-20 drowning mortality from 2000 to 2013 among 21 countries. Age-standardized drowning mortality data were obtained through the World Health Organization (WHO) Mortality Database. Twenty of the 21 included countries experienced a reduction in under-20 drowning mortality rate between 2000 and 2013, with decreases ranging from -80 to -13%. Detailed analysis by drowning method presented large variations in the cause of drowning across countries. Data were missing due to unspecified methods in some countries but, when known, drowning in natural bodies of water was the primary cause of child and adolescent drowning in Poland (56-92%), Cuba (53-81%), Venezuela (43-56%), and Japan (39-60%), while drowning in swimming pools and bathtubs was common in the United States (26-37%) and Japan (28-39%), respectively. We recommend efforts to raise the quality of drowning death reporting systems and discuss prevention strategies that may reduce child and adolescent drowning risk, both in individual countries and globally.
Keywords: child; drowning; mortality; trend.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Bhalla K., Hu G., Baker T.D., Baker S.P. Injuries among children: An unrecognized threat in low- and middle-income countries; Proceedings of the APHA 140th Annual Meeting & EXPO; San Francisco, CA, USA. 27–31 October 2012.
-
- Zhu Y., Xu G., Li H., Huang Y., Ding K., Chen J. Epidemiology and risk factors for nonfatal drowning in the migrant children. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health. 2015;46:1112–1123. - PubMed
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) GBD Compare Data Visualization. IHME, University of Washington; Seattle, WA, USA: 2016.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

