Prevalence and Genetic Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus argenteus Isolates Harboring Panton-Valentine Leukocidin, Enterotoxins, and TSST-1 Genes from Food Handlers in Myanmar
- PMID: 28777321
- PMCID: PMC5577575
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins9080241
Prevalence and Genetic Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus argenteus Isolates Harboring Panton-Valentine Leukocidin, Enterotoxins, and TSST-1 Genes from Food Handlers in Myanmar
Abstract
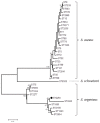
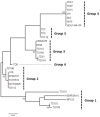
Asymptomatic carriers of toxigenic Staphylococcus aureus are potential source of diseases, including food poisoning. Toxigenic potential and genetic traits of colonizing S. aureus were investigated for 563 healthy food handlers in Myanmar. Carriage of S. aureus was found in 110 individuals (19.5%), and a total of 144 S. aureus isolates were recovered from nasal cavities (110 isolates) and hands (34 isolates). Panton-Valentine leucocidin genes (pvl) were detected in 18 isolates (12.5%), among which 11 isolates were classified into coa-VIa, agr type III, and ST1930 (CC96) that had been also detected in pvl-positive clinical isolates in Myanmar. A pvl-positive, ST2250 nasal isolate was identified as S. argenteus, a novel coagulase-positive staphylococcus species. Toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1) gene was detected in five pvl-negative isolates. All of the 144 isolates harbored at least one of the 21 enterotoxin(-like) gene(s). The most prevalent enterotoxin(-like) gene was selw (98%), followed by selx (97%), sei (28%), sely (28%), sem (26%), sel (24%), and sea and sec (22% each). Considerable genetic diversity with five groups was detected for selw. The present study revealed the relatively high rate of pvl, as well as the wide distribution of enterotoxin(-like) genes among colonizing S. aureus in Myanmar.
Keywords: Myanmar; Panton-Valentine leukocidin; Staphylococcus argenteus; Staphylococcus aureus; TSST-1; enterotoxin; enterotoxin-like gene; food handler.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

