Food Processing: The Influence of the Maillard Reaction on Immunogenicity and Allergenicity of Food Proteins
- PMID: 28777346
- PMCID: PMC5579628
- DOI: 10.3390/nu9080835
Food Processing: The Influence of the Maillard Reaction on Immunogenicity and Allergenicity of Food Proteins
Abstract
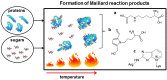
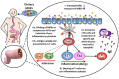
The majority of foods that are consumed in our developed society have been processed. Processing promotes a non-enzymatic reaction between proteins and sugars, the Maillard reaction (MR). Maillard reaction products (MRPs) contribute to the taste, smell and color of many food products, and thus influence consumers' choices. However, in recent years, MRPs have been linked to the increasing prevalence of diet- and inflammation-related non-communicable diseases including food allergy. Although during the last years a better understanding of immunogenicity of MRPs has been achieved, still only little is known about the structural/chemical characteristics predisposing MRPs to interact with antigen presenting cells (APCs). This report provides a comprehensive review of recent studies on the influence of the Maillard reaction on the immunogenicity and allergenicity of food proteins.
Keywords: Maillard reaction; Maillard reaction in food; Maillard reaction products (MRPs); advanced glycation end products (AGEs); allergenicity of AGEs; immunogenicity of AGEs.
Conflict of interest statement
RJJvN is an employee of FrieslandCampina. HFJS and MT declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Pereira R.N., Vicente A.A. Environmental impact of novel thermal and non-thermal technologies in food processing. Food Res. Int. 2010;43:1936–1943. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2009.09.013. - DOI
-
- Ling B., Tang J., Kong F., Mitcham E.J., Wang S. Kinetics of food quality changes during thermal processing: A review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2015;8:343–358. doi: 10.1007/s11947-014-1398-3. - DOI
-
- Sevenich R., Bark F., Kleinstueck E., Crews C., Pye C., Hradecky J., Reineke K., Lavilla M., Martinez-de-Maranon I., Briand J.C., et al. The impact of high pressure thermal sterilization on the microbiological stability and formation of food processing contaminants in selected fish systems and baby food puree at pilot scale. Food Control. 2015;50:539–547. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.09.050. - DOI
-
- Peng P., Song H., Zhang T., Addy M., Zhang Y., Cheng Y., Hatzenbeller R., Zhu X., Liu S., Liu Y., et al. Concentrated high intensity electric field (chief) system for non-thermal pasteurization of liquid foods: Modeling and simulation of fluid mechanics, electric analysis, and heat transfer. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2017;97:183–193. doi: 10.1016/j.compchemeng.2016.11.044. - DOI
-
- Halpin R.M., Duffy L., Cregenzán-Alberti O., Lyng J.G., Noci F. The effect of non-thermal processing technologies on microbial inactivation: An investigation into sub-lethal injury of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas fluorescens. Food Control. 2014;41:106–115. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.01.011. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

