Sulfide production and oxidation by heterotrophic bacteria under aerobic conditions
- PMID: 28777380
- PMCID: PMC5702731
- DOI: 10.1038/ismej.2017.125
Sulfide production and oxidation by heterotrophic bacteria under aerobic conditions
Abstract
Sulfide (H2S, HS- and S2-) oxidation to sulfite and thiosulfate by heterotrophic bacteria, using sulfide:quinone oxidoreductase (SQR) and persulfide dioxygenase (PDO), has recently been reported as a possible detoxification mechanism for sulfide at high levels. Bioinformatic analysis revealed that the sqr and pdo genes were common in sequenced bacterial genomes, implying the sulfide oxidation may have other physiological functions. SQRs have previously been classified into six types. Here we grouped PDOs into three types and showed that some heterotrophic bacteria produced and released H2S from organic sulfur into the headspace during aerobic growth, and others, for example, Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, with sqr and pdo did not release H2S. When the sqr and pdo genes were deleted, the mutants also released H2S. Both sulfide-oxidizing and non-oxidizing heterotrophic bacteria were readily isolated from various environmental samples. The sqr and pdo genes were also common in the published marine metagenomic and metatranscriptomic data, indicating that the genes are present and expressed. Thus, heterotrophic bacteria actively produce and consume sulfide when growing on organic compounds under aerobic conditions. Given their abundance on Earth, their contribution to the sulfur cycle should not be overlooked.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

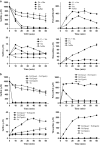
 In Figure 2d, control Ec(pMCS5): sulfide, ○ thiosulfate, □ and sulfane sulfur,
In Figure 2d, control Ec(pMCS5): sulfide, ○ thiosulfate, □ and sulfane sulfur,  Sulfide oxidation, polysulfide production and thiosulfate production by E. coli with cloned Zppdo, Bcpdo or Sapdo were essentially the same as Ec(pMCS5) (Data not shown).
Sulfide oxidation, polysulfide production and thiosulfate production by E. coli with cloned Zppdo, Bcpdo or Sapdo were essentially the same as Ec(pMCS5) (Data not shown).

References
-
- Alcolombri U, Ben-Dor S, Feldmesser E, Levin Y, Tawfik DS, Vardi A. (2015). MARINE SULFUR CYCLE. Identification of the algal dimethyl sulfide-releasing enzyme: a missing link in the marine sulfur cycle. Science 348: 1466–1469. - PubMed
-
- Amin S, Hmelo L, van Tol H, Durham B, Carlson L, Heal K et al. (2015). Interaction and signalling between a cosmopolitan phytoplankton and associated bacteria. Nature 522: 98–101. - PubMed
-
- Anandham R, Indiragandhi P, Madhaiyan M, Ryu KY, Jee HJ, Sa TM. (2008). Chemolithoautotrophic oxidation of thiosulfate and phylogenetic distribution of sulfur oxidation gene (soxB) in rhizobacteria isolated from crop plants. Res Microbiol 159: 579–589. - PubMed
-
- Clarke PH. (1953). Hydrogen sulphide production by bacteria. J Gen Microbiol 8: 397–407. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

