To What Extent Are the Terminal Stages of Sepsis, Septic Shock, Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome, and Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome Actually Driven by a Prion/Amyloid Form of Fibrin?
- PMID: 28778104
- PMCID: PMC6193370
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0037-1604108
To What Extent Are the Terminal Stages of Sepsis, Septic Shock, Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome, and Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome Actually Driven by a Prion/Amyloid Form of Fibrin?
Abstract
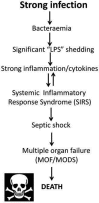
A well-established development of increasing disease severity leads from sepsis through systemic inflammatory response syndrome, septic shock, multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, and cellular and organismal death. Less commonly discussed are the equally well-established coagulopathies that accompany this. We argue that a lipopolysaccharide-initiated (often disseminated intravascular) coagulation is accompanied by a proteolysis of fibrinogen such that formed fibrin is both inflammatory and resistant to fibrinolysis. In particular, we argue that the form of fibrin generated is amyloid in nature because much of its normal α-helical content is transformed to β-sheets, as occurs with other proteins in established amyloidogenic and prion diseases. We hypothesize that these processes of amyloidogenic clotting and the attendant coagulopathies play a role in the passage along the aforementioned pathways to organismal death, and that their inhibition would be of significant therapeutic value, a claim for which there is considerable emerging evidence.
Thieme Medical Publishers 333 Seventh Avenue, New York, NY 10001, USA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Martin G S, Mannino D M, Eaton S, Moss M. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(16):1546–1554. - PubMed
-
- Ranieri V M, Thompson B T, Barie P S et al.Drotrecogin alfa (activated) in adults with septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(22):2055–2064. - PubMed
-
- Angus D C, van der Poll T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(09):840–851. - PubMed
-
- Dellinger R P, Levy M M, Rhodes A et al.Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Crit Care Med. 2013;41(02):580–637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

