Strategies for optimizing BioNano and Dovetail explored through a second reference quality assembly for the legume model, Medicago truncatula
- PMID: 28778149
- PMCID: PMC5545040
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-017-3971-4
Strategies for optimizing BioNano and Dovetail explored through a second reference quality assembly for the legume model, Medicago truncatula
Abstract
Background: Third generation sequencing technologies, with sequencing reads in the tens- of kilo-bases, facilitate genome assembly by spanning ambiguous regions and improving continuity. This has been critical for plant genomes, which are difficult to assemble due to high repeat content, gene family expansions, segmental and tandem duplications, and polyploidy. Recently, high-throughput mapping and scaffolding strategies have further improved continuity. Together, these long-range technologies enable quality draft assemblies of complex genomes in a cost-effective and timely manner.
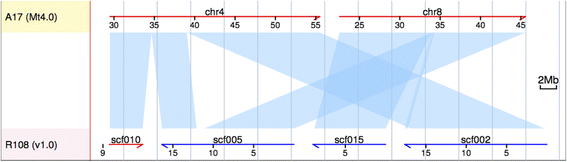
Results: Here, we present high quality genome assemblies of the model legume plant, Medicago truncatula (R108) using PacBio, Dovetail Chicago (hereafter, Dovetail) and BioNano technologies. To test these technologies for plant genome assembly, we generated five assemblies using all possible combinations and ordering of these three technologies in the R108 assembly. While the BioNano and Dovetail joins overlapped, they also showed complementary gains in continuity and join numbers. Both technologies spanned repetitive regions that PacBio alone was unable to bridge. Combining technologies, particularly Dovetail followed by BioNano, resulted in notable improvements compared to Dovetail or BioNano alone. A combination of PacBio, Dovetail, and BioNano was used to generate a high quality draft assembly of R108, a M. truncatula accession widely used in studies of functional genomics. As a test for the usefulness of the resulting genome sequence, the new R108 assembly was used to pinpoint breakpoints and characterize flanking sequence of a previously identified translocation between chromosomes 4 and 8, identifying more than 22.7 Mb of novel sequence not present in the earlier A17 reference assembly.
Conclusions: Adding Dovetail followed by BioNano data yielded complementary improvements in continuity over the original PacBio assembly. This strategy proved efficient and cost-effective for developing a quality draft assembly compared to traditional reference assemblies.
Keywords: BioNano; Dovetail; Genome assembly; Medicago truncatula; Next generation sequencing; PacBio.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Medicago germplasm resources (seed) were obtained and used, with permission, from Jean-Marie Prosperi at Unité mixte de recherche / Amélioration génétique et adaptation des plantes méditerranéennes et tropicales (UMR-AGAP) at INRA-Montpellier, France.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

