Intermittent hypoxia-induced cardiomyopathy and its prevention by Nrf2 and metallothionein
- PMID: 28778483
- PMCID: PMC7453314
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.07.031
Intermittent hypoxia-induced cardiomyopathy and its prevention by Nrf2 and metallothionein
Abstract
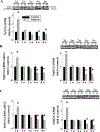
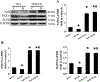
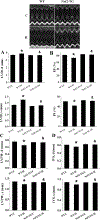
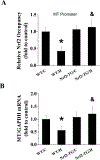
The mechanism for intermittent hypoxia (IH)-induced cardiomyopathy remains obscure. We reported the prevention of acute and chronic IH-induced cardiac damage by selective cardiac overexpression of metallothionein (MT). Herein we defined that MT-mediated protection from IH-cardiomyopathy is via activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a critical redox-balance controller in the body. For this, mice were exposed to IH for 3 days (acute) or 4 or 8 weeks (chronic). Cardiac Nrf2 and MT expression in response to IH were significantly increased acutely yet decreased chronically. Interestingly, cardiac overexpression (Nrf2-TG) or global deletion of the Nrf2 gene (Nrf2-KO) made mice highly resistant or highly susceptible, respectively, to IH-induced cardiomyopathy and MT expression. Mechanistically, 4-week IH exposure significantly decreased cardiac Nrf2 binding to the MT gene promoter, and thus, depressed both MT transcription and translation in WT mice but not Nrf2-TG mice. Likewise, cardiac MT overexpression prevented chronic IH-induced cardiomyopathy and down-regulation of Nrf2 likely via activation of a PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β/Fyn-dependent signaling pathway. These results reveal an integrated relationship between cardiac Nrf2 and MT expression in response to IH -- acute compensatory up-regulation followed by chronic down-regulation and cardiomyopathy. Cardiac overexpression of either Nrf2 or MT offered cardioprotection from IH via complicated PI3K/Akt/GSK3B/Fyn signaling. Potential therapeutics may target either Nrf2 or MT to prevent chronic IH-induced cardiomyopathy.
Keywords: Intermittent hypoxia; Metallothionein; Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; Obstructive sleep apnea; Redox regulation.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in this work.
Figures



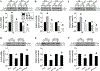




Similar articles
-
Nrf2 expression and function, but not MT expression, is indispensable for sulforaphane-mediated protection against intermittent hypoxia-induced cardiomyopathy in mice.Redox Biol. 2018 Oct;19:11-21. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.07.014. Epub 2018 Jul 21. Redox Biol. 2018. PMID: 30096613 Free PMC article.
-
Sulforaphane prevents angiotensin II-induced cardiomyopathy by activation of Nrf2 via stimulating the Akt/GSK-3ß/Fyn pathway.Redox Biol. 2018 May;15:405-417. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.12.016. Epub 2018 Jan 2. Redox Biol. 2018. PMID: 29353218 Free PMC article.
-
Metallothionein deletion exacerbates intermittent hypoxia-induced renal injury in mice.Toxicol Lett. 2015 Jan 22;232(2):340-8. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.11.015. Epub 2014 Nov 15. Toxicol Lett. 2015. PMID: 25448280
-
Diabetic cardiomyopathy and its prevention by metallothionein: experimental evidence, possible mechanisms and clinical implications.Curr Med Chem. 2007;14(20):2193-203. doi: 10.2174/092986707781389646. Curr Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17691957 Review.
-
PI3K/Akt-Nrf2 and Anti-Inflammation Effect of Macrolides in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Curr Drug Metab. 2019;20(4):301-304. doi: 10.2174/1389200220666190227224748. Curr Drug Metab. 2019. PMID: 30827233 Review.
Cited by
-
Nrf2 for cardiac protection: pharmacological options against oxidative stress.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Sep;42(9):729-744. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2021.06.005. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34332753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination of Broccoli Sprout Extract and Zinc Provides Better Protection against Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Cardiomyopathy Than Monotherapy in Mice.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Dec 14;2019:2985901. doi: 10.1155/2019/2985901. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31934264 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis of the inflammation in diabetic cardiomyopathy.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Dec 13;9:1006213. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1006213. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36582738 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of Metallothionein Expression After Exposure to Conventional Cigarette Smoke but Not Electronic Cigarette (ECIG)-Generated Aerosol in Caenorhabditis elegans.Front Physiol. 2018 Apr 23;9:426. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00426. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29740339 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium Tanshinone IIA Sulfonate Attenuates Tumor Oxidative Stress and Promotes Apoptosis in an Intermittent Hypoxia Mouse Model.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1533033820928073. doi: 10.1177/1533033820928073. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 32431212 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gottlieb DJ, Whitney CW, Bonekat WH, Iber C, James GD, Lebowitz M, Nieto FJ, Rosenberg CE, Relation of sleepiness to respiratory disturbance index: the Sleep Heart Health Study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 159 (1999) 502–507. - PubMed
-
- Mazza S, Pepin JL, Naegele B, Plante J, Deschaux C, Levy P, Most obstructive sleep apnoea patients exhibit vigilance and attention deficits on an extended battery of tests. Eur Respir J 25 (2005) 75–80. - PubMed
-
- Leung RS, Bradley TD, Sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164 (2001) 2147–2165. - PubMed
-
- Young T, Peppard PE, Gottlieb DJ, Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea: a population health perspective. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine 165 (2002) 1217–1239. - PubMed
-
- Nieto FJ, Young TB, Lind BK, Shahar E, Samet JM, Redline S, D’Agostino RB, Newman AB, Lebowitz MD, Pickering TG, Association of sleep-disordered breathing, sleep apnea, and hypertension in a large community-based study. Sleep Heart Health Study. JAMA 283 (2000) 1829–1836. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

