Lipoprotein Receptor-related Protein 6 Signaling is Necessary for Vasculogenic Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells
- PMID: 28778505
- PMCID: PMC5657009
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2017.06.006
Lipoprotein Receptor-related Protein 6 Signaling is Necessary for Vasculogenic Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells
Abstract
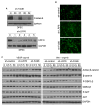
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of Wnt signaling through lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6) and Frizzled6 on the endothelial differentiation of dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs). DPSCs were stably transduced with enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP)-tagged lentiviral vectors (short hairpin RNA-LRP6, short hairpin RNA-Frizzled6, or empty vector controls). We evaluated the effects of LRP6 and Frizzled6 on expression of endothelial markers and on capillary tube formation mediated by DPSCs induced with recombinant human Wnt1 (rhWnt1) and/or recombinant human vascular endothelial growth factor165 (rhVEGF165). In vivo, tooth slices/scaffolds were seeded with LRP6-silenced, Frizzled6-silenced, or vector control DPSC cells and transplanted into immunodeficient mice. The density of blood vessels generated by DPSCs differentiated into vascular endothelial cells was analyzed by immunohistochemistry for EGFP. The rhWnt1 and rhVEGF165 induced expression of active β-catenin in control DPSCs and in Frizzled6-silenced DPSCs, but not in LRP6-silenced DPSCs. Furthermore, VEGF and interleukin-8 were downregulated in LRP6-silenced DPSCs, but not in control DPSCs or in Frizzled6-silenced DPSCs (P < .05). Likewise, rhWnt1 and rhVEGF165 induced expression of the endothelial marker VEGF receptor-2 in control DPSCs and in Frizzled6-silenced DPSCs, but not in LRP6-silenced DPSCs. These data correlated with a trend for lower density of capillary sprouts generated by LRP6-silenced DPSCs when compared with control DPSCs in Matrigel. In vivo, tooth slice/scaffolds seeded with DPSC-short hairpinRNA-LRP6 cells showed lower density of human blood vessels (ie, EGFP-positive blood vessels), when compared with tooth slice/scaffolds seeded with vector control cells (P < .05). Collectively, these data demonstrated that LRP6 signaling is necessary for the vasculogenic differentiation of human DPSCs.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Wnt; cell fate; regenerative endodontics; tissue engineering.
Copyright © 2017 American Association of Endodontists. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Nakashima M, Akamine A. The application of tissue engineering to regeneration of pulp and dentin in endodontics. J Endod. 2005;31:711–8. - PubMed
-
- Nör JE. Tooth regeneration in operative dentistry. Oper Dent. 2006;31:633–2. - PubMed
-
- Brey EM, Uriel S, Greisler HP, McIntire LV. Therapeutic neovascularization: contributions from bioengineering. Tissue Eng. 2005;11:567–84. - PubMed
-
- Gronthos S, Brahim J, Li W, et al. Stem cell properties of human dental pulp stem cells. J Dent Res. 2002;81:531–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

