Chronic fluoxetine ameliorates adolescent chronic nicotine exposure-induced long-term adult deficits in trace conditioning
- PMID: 28778833
- PMCID: PMC5757519
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.07.033
Chronic fluoxetine ameliorates adolescent chronic nicotine exposure-induced long-term adult deficits in trace conditioning
Abstract
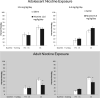
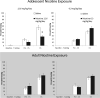
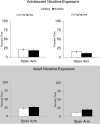
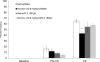
Development of the brain, including the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus, continues through adolescence. Chronic nicotine exposure during adolescence may contribute to long-term deficits in forebrain-dependent learning. It is unclear if these deficits emerge immediately after exposure and if they can be ameliorated. In this study, C57BL/6J mice were treated with chronic nicotine (6.3 or 12.6 mg/kg/day) over 12 days beginning at adolescence, postnatal day (PND) 38, or adulthood, PND 56-63 ± 3. We investigated the effects of short-term (24 h) abstinence on trace fear conditioning and found that adult treatment resulted in deficits (6.3 and 12.6 mg/kg/day), but adolescent chronic nicotine treatment had no effect. In contrast, adolescent treatment with chronic nicotine (12.6 mg/kg/day) elicited a long-term (30 days) learning deficit, but adult chronic nicotine treatment did not. Using the elevated plus maze (EPM) we found no long-term changes in anxiety-related behavior after chronic nicotine exposure at either time-point. We investigated if chronic fluoxetine (FLX) could ameliorate adolescent chronic nicotine-associated long-term deficits in trace conditioning. We found that chronic FLX (160 mg/L) in drinking water ameliorated the long-term deficit in trace fear conditioning associated with nicotine exposure during adolescence. Additionally, in the same animals, we examined changes in total BDNF protein in the dorsal hippocampus (DH), ventral hippocampus (VH), and prefrontal cortex (PFC). Chronic FLX increased DH BDNF. Our data indicate nicotine administration during adolescence leads to late onset, long-lasting deficits in hippocampus-dependent learning that chronic FLX treatment ameliorate.
Keywords: Addiction; Adolescence; Cognition; Fluoxetine; Learning; Nicotine.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Long-term effects of chronic nicotine on emotional and cognitive behaviors and hippocampus cell morphology in mice: comparisons of adult and adolescent nicotine exposure.Eur J Neurosci. 2016 Nov;44(10):2818-2828. doi: 10.1111/ejn.13398. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Eur J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27623427 Free PMC article.
-
Concentration- and age-dependent effects of chronic caffeine on contextual fear conditioning in C57BL/6J mice.Behav Brain Res. 2016 Feb 1;298(Pt A):69-77. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.03.045. Epub 2015 Mar 28. Behav Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 25827925 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of adolescent administration of fluoxetine on novel object recognition memory, anxiety-like behaviors, and hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor level.Life Sci. 2020 Nov 1;260:118338. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118338. Epub 2020 Aug 22. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32841662
-
Cellular, molecular, and genetic substrates underlying the impact of nicotine on learning.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014 Jan;107:108-32. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2013.08.004. Epub 2013 Aug 22. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 23973448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Associative learning, the hippocampus, and nicotine addiction.Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2008 Jan;1(1):9-19. doi: 10.2174/1874473710801010009. Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2008. PMID: 19630701 Review.
Cited by
-
Stress and nicotine during adolescence disrupts adult hippocampal-dependent learning and alters stress reactivity.Addict Biol. 2020 May;25(3):e12769. doi: 10.1111/adb.12769. Epub 2019 May 16. Addict Biol. 2020. PMID: 31099135 Free PMC article.
-
Histone serotonylation in dorsal raphe nucleus contributes to stress- and antidepressant-mediated gene expression and behavior.Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 13;15(1):5042. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49336-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38871707 Free PMC article.
-
Age- and Genotype-Dependent Effects of Chronic Nicotine on Presenilin1/2 Double Knockout Mice: From Behavior to Molecular Pathways.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2024;21(11):817-832. doi: 10.2174/0115672050363992250127072919. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2024. PMID: 39936411
-
Effects of chronic fluoxetine treatment on anxiety- and depressive-like behaviors in adolescent rodents - systematic review and meta-analysis.Pharmacol Rep. 2022 Oct;74(5):920-946. doi: 10.1007/s43440-022-00420-w. Epub 2022 Sep 24. Pharmacol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36151445 Free PMC article.
-
Interstrain differences in adolescent fear conditioning after acute alcohol exposure.Brain Res Bull. 2023 Mar;194:35-44. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2023.01.006. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Brain Res Bull. 2023. PMID: 36681252 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abreu-Villaça Y, Nunes F, Queiroz-Gomes F, do E, Manhães AC, Filgueiras CC. Combined exposure to nicotine and ethanol in adolescent mice differentially affects anxiety levels during exposure, short-Term, and long-term withdrawal. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2007;33:599–610. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1301429. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abreu-Villaca Y, Seidler FJ, Qiao D, Tate CA, Cousins MM, Thillai I, Slotkin TA. Short-term adolescent nicotine exposure has immediate and persistent effects on cholinergic systems: Critical periods, patterns of exposure, dose thresholds. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2003;28:1935–1949. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300221. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

