Indole Biodegradation in Acinetobacter sp. Strain O153: Genetic and Biochemical Characterization
- PMID: 28778892
- PMCID: PMC5601350
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01453-17
Indole Biodegradation in Acinetobacter sp. Strain O153: Genetic and Biochemical Characterization
Abstract
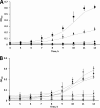
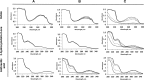
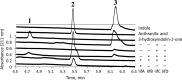
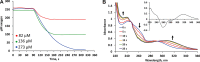
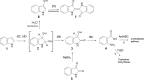
Indole is a molecule of considerable biochemical significance, acting as both an interspecies signal molecule and a building block of biological elements. Bacterial indole degradation has been demonstrated for a number of cases; however, very little is known about genes and proteins involved in this process. This study reports the cloning and initial functional characterization of genes (iif and ant cluster) responsible for indole biodegradation in Acinetobacter sp. strain O153. The catabolic cascade was reconstituted in vitro with recombinant proteins, and each protein was assigned an enzymatic function. Degradation starts with oxidation, mediated by the IifC and IifD flavin-dependent two-component oxygenase system. Formation of indigo is prevented by IifB, and the final product, anthranilic acid, is formed by IifA, an enzyme which is both structurally and functionally comparable to cofactor-independent oxygenases. Moreover, the iif cluster was identified in the genomes of a wide range of bacteria, suggesting the potential of widespread Iif-mediated indole degradation. This work provides novel insights into the genetic background of microbial indole biodegradation.IMPORTANCE The key finding of this research is identification of the genes responsible for microbial biodegradation of indole, a toxic N-heterocyclic compound. A large amount of indole is present in urban wastewater and sewage sludge, creating a demand for an efficient and eco-friendly means to eliminate this pollutant. A common strategy of oxidizing indole to indigo has the major drawback of producing insoluble material. Genes and proteins of Acinetobacter sp. strain O153 (DSM 103907) reported here pave the way for effective and indigo-free indole removal. In addition, this work suggests possible novel means of indole-mediated bacterial interactions and provides the basis for future research on indole metabolism.
Keywords: Acinetobacter; bacterial metabolism; bacterial signaling; biodegradation; cofactor-independent oxygenases; indole.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biodegradation and Biotransformation of Indole: Advances and Perspectives.Front Microbiol. 2018 Nov 1;9:2625. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02625. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30443243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of the Metabolites of Indole Degraded by an Isolated Acinetobacter pittii L1.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:2564363. doi: 10.1155/2017/2564363. Epub 2017 Dec 13. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 29392129 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and functional gene analysis of a newly isolated indole-degrading bacterium Burkholderia sp. IDO3.J Hazard Mater. 2019 Apr 5;367:144-151. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.12.068. Epub 2018 Dec 19. J Hazard Mater. 2019. PMID: 30594713
-
Detoxification of Indole by an Indole-Induced Flavoprotein Oxygenase from Acinetobacter baumannii.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 21;10(9):e0138798. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138798. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26390211 Free PMC article.
-
Upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor--a review.Indian J Environ Health. 2001 Apr;43(2):1-82. Indian J Environ Health. 2001. PMID: 12397675 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and Characterization of Indole-Responsive Whole-Cell Biosensor Based on the Inducible Gene Expression System from Pseudomonas putida KT2440.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 22;23(9):4649. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094649. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563040 Free PMC article.
-
A Review: The Styrene Metabolizing Cascade of Side-Chain Oxygenation as Biotechnological Basis to Gain Various Valuable Compounds.Front Microbiol. 2018 Mar 22;9:490. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00490. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29623070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Analysis of Indole and Skatole Decomposition Metabolism in Acinetobacter piscicola p38 Utilizing Biochemical and Omics Approaches.Microorganisms. 2024 Aug 29;12(9):1792. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12091792. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39338467 Free PMC article.
-
Biodegradation and Biotransformation of Indole: Advances and Perspectives.Front Microbiol. 2018 Nov 1;9:2625. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02625. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30443243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of an indole biodegradation gene cluster from Providencia rettgeri and its contribution in selectively biosynthesizing Tyrian purple.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Jan 10;10:1109929. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1109929. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36704308 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

