Modulation of mesenteric collecting lymphatic contractions by σ1-receptor activation and nitric oxide production
- PMID: 28778917
- PMCID: PMC5668603
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00702.2016
Modulation of mesenteric collecting lymphatic contractions by σ1-receptor activation and nitric oxide production
Abstract
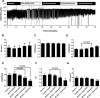
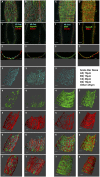
Recently, it has been reported that a σ-receptor antagonist could reduce inflammation-induced edema. Lymphatic vessels play an essential role in removing excess interstitial fluid. We tested the hypothesis that activation of σ-receptors would reduce or weaken collecting lymphatic contractions. We used isolated, cannulated rat mesenteric collecting lymphatic vessels to study contractions in response to the σ-receptor agonist afobazole in the absence and presence of different σ-receptor antagonists. We used RT-PCR and Western blot analysis to investigate whether these vessels express the σ1-receptor and immunofluorescence confocal microscopy to examine localization of the σ1-receptor in the collecting lymphatic wall. Using N-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (l-NAME) pretreatment before afobazole in isolated lymphatics, we tested the role of nitric oxide (NO) signaling. Finally, we used 4-amino-5-methylamino-2',7'-difluorofluorescein diacetate fluorescence as an indicator to test whether afobazole increases NO release in cultured lymphatic endothelial cells. Our results show that afobazole (50-150 µM) elevated end-systolic diameter and generally reduced pump efficiency and that this response could be partially blocked by the σ1-receptor antagonists BD 1047 and BD 1063 but not by the σ2-receptor antagonist SM-21. σ1-Receptor mRNA and protein were detected in lysates from isolated rat mesenteric collecting lymphatics. Confocal images with anti-σ1-receptor antibody labeling suggested localization in the lymphatic endothelium. Blockade of NO synthases with l-NAME inhibited the effects of afobazole. Finally, afobazole elicited increases in NO production from cultured lymphatic endothelial cells. Our findings suggest that the σ1-receptor limits collecting lymphatic pumping through a NO-dependent mechanism.NEW & NOTEWORTHY Relatively little is known about the mechanisms that govern contractions of lymphatic vessels. σ1-Receptor activation has been shown to reduce the fractional pump flow of isolated rat mesenteric collecting lymphatics. The σ1-receptor was localized mainly in the endothelium, and blockade of nitric oxide synthase inhibited the effects of afobazole.
Keywords: afobazole; collecting lymphatic; lymphatic endothelium; nitric oxide; σ1-receptor.
Copyright © 2017 the American Physiological Society.
Figures






References
-
- Atchison DJ, Johnston MG. Role of extra- and intracellular Ca2+ in the lymphatic myogenic response. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 272: R326–R333, 1997. - PubMed
-
- Benoit JN, Zawieja DC, Goodman AH, Granger HJ. Characterization of intact mesenteric lymphatic pump and its responsiveness to acute edemagenic stress. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 257: H2059–H2069, 1989. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

