From Ras to Rap and Back, a Journey of 35 Years
- PMID: 28778969
- PMCID: PMC5793741
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a031468
From Ras to Rap and Back, a Journey of 35 Years
Abstract
Our laboratory has studied Ras and Ras-like proteins since the discovery of the Ras oncogene 35 years ago. In this review, I will give an account of what we have done in these 35 years and indicate the main papers that have guided our research. Our efforts started with the early analysis of mutant Ras in human tumors followed by deciphering of the role of Ras in signal transduction pathways. In an attempt to interfere in Ras signaling we turned to Rap proteins. These proteins are the closest relatives of Ras and were initially identified as Ras antagonists. However, our studies revealed that the Rap signaling network primarily is involved in spatiotemporal control of cell adhesion, in part through regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. More recently we returned to Ras, trying to interfere in Ras signaling by combinatorial drug testing using the organoid technology.
Copyright © 2018 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures

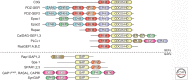

References
-
- Almoguera C, Shibata D, Forrester K, Martin J, Arnheim N, Perucho M. 1988. Most human carcinomas of the exocrine pancreas contain mutant c-K-ras genes. Cell 53: 549–554. - PubMed
-
- Altschuler DL, Peterson SN, Ostrowski MC, Lapetina EG. 1995. Cyclic AMP-dependent activation of Rap1b. J Biol Chem 270: 10373–10376. - PubMed
-
- Baas AF, Kuipers J, van der Wel NN, Batlle E, Koerten HK, Peters PJ, Clevers HC. 2004. Complete polarization of single intestinal epithelial cells upon activation of LKB1 by STRAD. Cell 116: 457–466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
