CDK5 Regulatory Subunit-Associated Protein 1-like 1 Negatively Regulates Adipocyte Differentiation through Activation of Wnt Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 28779110
- PMCID: PMC5544666
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-06469-5
CDK5 Regulatory Subunit-Associated Protein 1-like 1 Negatively Regulates Adipocyte Differentiation through Activation of Wnt Signaling Pathway
Abstract
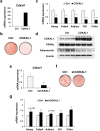
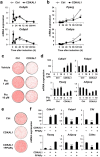
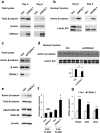
CDK5 Regulatory Subunit-Associated Protein 1-like 1 (CDKAL1) was identified as a susceptibility gene for type 2 diabetes and body mass index in genome-wide association studies. Although it was reported that CDKAL1 is a methylthiotransferase essential for tRNALys(UUU) and faithful translation of proinsulin generated in pancreatic β cells, the role of CDKAL1 in adipocytes has not been understood well. In this study, we found that CDKAL1 is expressed in adipose tissue and its expression is increased during differentiation. Stable overexpression of CDKAL1, however, inhibited adipocyte differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells, whereas knockdown of CDKAL1 promoted differentiation. CDKAL1 increased protein levels of β-catenin and its active unphosphorylated form in the nucleus, thereby promoting Wnt target gene expression, suggesting that CDKAL1 activated the Wnt/β-catenin pathway-a well-characterized inhibitory regulator of adipocyte differentiation. Mutant experiments show that conserved cysteine residues of Fe-S clusters of CDKAL1 are essential for its anti-adipogenic action. Our results identify CDKAL1 as novel negative regulator of adipocyte differentiation and provide insights into the link between CDKAL1 and metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

