Epigenetic regulation of starvation-induced autophagy in Drosophila by histone methyltransferase G9a
- PMID: 28779125
- PMCID: PMC5544687
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-07566-1
Epigenetic regulation of starvation-induced autophagy in Drosophila by histone methyltransferase G9a
Abstract
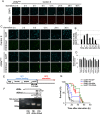
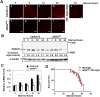
Epigenetics is now emerging as a key regulation in response to various stresses. We herein identified the Drosophila histone methyltransferase G9a (dG9a) as a key factor to acquire tolerance to starvation stress. The depletion of dG9a led to high sensitivity to starvation stress in adult flies, while its overexpression induced starvation stress resistance. The catalytic domain of dG9a was not required for starvation stress resistance. dG9a plays no apparent role in tolerance to other stresses including heat and oxidative stresses. Metabolomic approaches were applied to investigate global changes in the metabolome due to the loss of dG9a during starvation stress. The results obtained indicated that dG9a plays an important role in maintaining energy reservoirs including amino acid, trehalose, glycogen, and triacylglycerol levels during starvation. Further investigations on the underlying mechanisms showed that the depletion of dG9a repressed starvation-induced autophagy by controlling the expression level of Atg8a, a critical gene for the progression of autophagy, in a different manner to that in cancer cells. These results indicate a positive role for dG9a in starvation-induced autophagy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

