Analysis of the R1b-DF27 haplogroup shows that a large fraction of Iberian Y-chromosome lineages originated recently in situ
- PMID: 28779148
- PMCID: PMC5544771
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-07710-x
Analysis of the R1b-DF27 haplogroup shows that a large fraction of Iberian Y-chromosome lineages originated recently in situ
Abstract
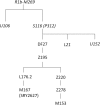
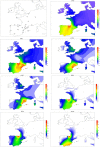
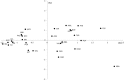
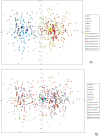
Haplogroup R1b-M269 comprises most Western European Y chromosomes; of its main branches, R1b-DF27 is by far the least known, and it appears to be highly prevalent only in Iberia. We have genotyped 1072 R1b-DF27 chromosomes for six additional SNPs and 17 Y-STRs in population samples from Spain, Portugal and France in order to further characterize this lineage and, in particular, to ascertain the time and place where it originated, as well as its subsequent dynamics. We found that R1b-DF27 is present in frequencies ~40% in Iberian populations and up to 70% in Basques, but it drops quickly to 6-20% in France. Overall, the age of R1b-DF27 is estimated at ~4,200 years ago, at the transition between the Neolithic and the Bronze Age, when the Y chromosome landscape of W Europe was thoroughly remodeled. In spite of its high frequency in Basques, Y-STR internal diversity of R1b-DF27 is lower there, and results in more recent age estimates; NE Iberia is the most likely place of origin of DF27. Subhaplogroup frequencies within R1b-DF27 are geographically structured, and show domains that are reminiscent of the pre-Roman Celtic/Iberian division, or of the medieval Christian kingdoms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effective resolution of the Y chromosome sublineages of the Iberian haplogroup R1b-DF27 with forensic purposes.Int J Legal Med. 2019 Jan;133(1):17-23. doi: 10.1007/s00414-018-1936-z. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Int J Legal Med. 2019. PMID: 30229332
-
Characterization of the Iberian Y chromosome haplogroup R-DF27 in Northern Spain.Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2017 Mar;27:142-148. doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2016.12.013. Epub 2016 Dec 29. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2017. PMID: 28073088
-
Paternal lineages in southern Iberia provide time frames for gene flow from mainland Europe and the Mediterranean world.Ann Hum Biol. 2019 Feb;46(1):63-76. doi: 10.1080/03014460.2019.1587507. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Ann Hum Biol. 2019. PMID: 30822152
-
Phylogeographic review of Y chromosome haplogroups in Europe.Int J Legal Med. 2021 Sep;135(5):1675-1684. doi: 10.1007/s00414-021-02644-6. Epub 2021 Jul 3. Int J Legal Med. 2021. PMID: 34216266 Review.
-
Genetic analysis of 17 Y-STRs in a Mestizo population from the Central Valley of Mexico.Hum Biol. 2014 Fall;86(4):289-312. doi: 10.13110/humanbiology.86.4.0289. Hum Biol. 2014. PMID: 25959695 Review.
Cited by
-
Delineating the dispersal of Y-chromosome sub-haplogroup O2a2b-P164 among Austronesian-speaking populations.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 24;14(1):2066. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52293-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38267477 Free PMC article.
-
Y-chromosome analysis recapitulates key events of Mediterranean populations.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 26;10(16):e35329. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35329. eCollection 2024 Aug 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39220888 Free PMC article.
-
Contrasting maternal and paternal genetic histories among five ethnic groups from Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 19;12(1):1027. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05076-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35046511 Free PMC article.
-
A Transient Pulse of Genetic Admixture from the Crusaders in the Near East Identified from Ancient Genome Sequences.Am J Hum Genet. 2019 May 2;104(5):977-984. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.03.015. Epub 2019 Apr 18. Am J Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 31006515 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome-Y haplogroups in Asturias (Northern Spain) and their association with severe COVID-19.Mol Genet Genomics. 2024 May 4;299(1):49. doi: 10.1007/s00438-024-02143-4. Mol Genet Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38704518 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Semino, O. et al. The genetic legacy of Paleolithic Homo sapiens sapiens in extant Europeans: a Y chromosome perpective. 290, 1155–1159 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

