Metabolomics window into diabetic complications
- PMID: 28779528
- PMCID: PMC5835462
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.12723
Metabolomics window into diabetic complications
Abstract
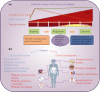
Diabetes has become a major global health problem. The elucidation of characteristic metabolic alterations during the diabetic progression is critical for better understanding its pathogenesis, and identifying potential biomarkers and drug targets. Metabolomics is a promising tool to reveal the metabolic changes and the underlying mechanism involved in the pathogenesis of diabetic complications. The present review provides an update on the application of metabolomics in diabetic complications, including diabetic coronary artery disease, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy and diabetic neuropathy, and this review provides notes on the prevention and prediction of diabetic complications.
Keywords: Biomarker; Diabetic complications; Metabolomics.
© 2017 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes Investigation published by Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes (AASD) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Evans JL, Goldfine ID, Maddux BA, et al Oxidative stress and stress‐activated signaling pathways: a unifying hypothesis of type 2 diabetes. Endocr Rev 2002; 23: 599–622. - PubMed
-
- Spranger J, Kroke A, Mohlig M, et al Inflammatory cytokines and the risk to develop type 2 diabetes: results of the prospective population‐based European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC)‐Potsdam Study. Diabetes 2003; 52: 812–817. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

