Evaluation and Management of Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections
- PMID: 28779832
- PMCID: PMC5656282
- DOI: 10.1016/j.idc.2017.05.011
Evaluation and Management of Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections
Abstract
Despite advances in antibiotic and surgical management and supportive care for necrotizing soft tissue infections, morbidity and mortality remain substantial. Although there are clinical practice guidelines in place, there still remains much variability in choice and duration of antibiotic therapy, time to initial surgical debridement, and use of adjuvant medical therapies. This article offers an overview of necrotizing soft tissue infections with a focus on current diagnostic and treatment modalities.
Keywords: Gangrene; Necrotizing fasciitis; Sepsis; Soft tissue infection.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
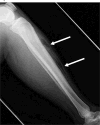
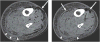
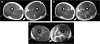
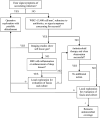
Figures


References
-
- Wilson B. Necrotizing fasciitis. Am Surg. 1952;18:416–31. - PubMed
-
- Yilmazlar T, Ozturk E, Alsoy A, et al. Necrotizing soft tissue infections: APACHE II score, dissemination, and survival. World J Surg. 2007;31:1858–1862. - PubMed
-
- Miller AT, Saadai P, Greenstein A, et al. Postprocedural necrotizing fasciitis: A 10-year retrospective review. Am Surg. 2008;74:405–409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

