Paths from DNA damage and signaling to genome rearrangements via homologous recombination
- PMID: 28779875
- PMCID: PMC9157578
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2017.07.008
Paths from DNA damage and signaling to genome rearrangements via homologous recombination
Abstract
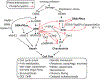
DNA damage is a constant threat to genome integrity. DNA repair and damage signaling networks play a central role maintaining genome stability, suppressing tumorigenesis, and determining tumor response to common cancer chemotherapeutic agents and radiotherapy. DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are critical lesions induced by ionizing radiation and when replication forks encounter damage. DSBs can result in mutations and large-scale genome rearrangements reflecting mis-repair by non-homologous end joining or homologous recombination. Ionizing radiation induces genetic change immediately, and it also triggers delayed events weeks or even years after exposure, long after the initial damage has been repaired or diluted through cell division. This review covers DNA damage signaling and repair pathways and cell fate following genotoxic insult, including immediate and delayed genome instability and cell survival/cell death pathways.
Keywords: DNA damage; DNA repair; Genome instability; Radiation.
Copyright © 2017. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Roles of homologous recombination in response to ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage.Int J Radiat Biol. 2023;99(6):903-914. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2021.1956001. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Int J Radiat Biol. 2023. PMID: 34283012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic rearrangements induced by unscheduled DNA double strand breaks in somatic mammalian cells.FEBS J. 2017 Aug;284(15):2324-2344. doi: 10.1111/febs.14053. Epub 2017 Mar 22. FEBS J. 2017. PMID: 28244221 Review.
-
EEPD1 Rescues Stressed Replication Forks and Maintains Genome Stability by Promoting End Resection and Homologous Recombination Repair.PLoS Genet. 2015 Dec 18;11(12):e1005675. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005675. eCollection 2015 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26684013 Free PMC article.
-
One end to rule them all: Non-homologous end-joining and homologous recombination at DNA double-strand breaks.Br J Radiol. 2020 Nov 1;93(1115):20191054. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20191054. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Br J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32105514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quality control of homologous recombination.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Oct;71(19):3779-97. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1649-5. Epub 2014 May 25. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24858417 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammation-induced DNA damage, mutations and cancer.DNA Repair (Amst). 2019 Nov;83:102673. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2019.102673. Epub 2019 Jul 25. DNA Repair (Amst). 2019. PMID: 31387777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subsequent Neoplasm Risk Associated With Rare Variants in DNA Damage Response and Clinical Radiation Sensitivity Syndrome Genes in the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study.JCO Precis Oncol. 2020 Aug 21;4:PO.20.00141. doi: 10.1200/PO.20.00141. eCollection 2020. JCO Precis Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32923912 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of homologous recombination in response to ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage.Int J Radiat Biol. 2023;99(6):903-914. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2021.1956001. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Int J Radiat Biol. 2023. PMID: 34283012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metnase and EEPD1: DNA Repair Functions and Potential Targets in Cancer Therapy.Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 28;12:808757. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.808757. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35155245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The DNA Endonuclease Mus81 Regulates ZEB1 Expression and Serves as a Target of BET4 Inhibitors in Gastric Cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2019 Aug;18(8):1439-1450. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0833. Epub 2019 May 29. Mol Cancer Ther. 2019. PMID: 31142662 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carr AM, Lambert S, Replication stress-induced genome instability: the dark side of replication maintenance by homologous recombination, J. Mol. Biol, 425 (2013) 4733–4744. - PubMed
-
- Loucas BD, Cornforth MN, Complex chromosome exchanges induced by gamma rays in human lymphocytes: an mFISH study, Radiat. Res, 155 (2001) 660–671. - PubMed
-
- Albertson DG, Gene amplification in cancer, Trends Genet, 22 (2006) 447–455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

