Activated Tissue-Resident Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Regulate Natural Killer Cell Immune and Tissue-Regenerative Function
- PMID: 28781075
- PMCID: PMC5599186
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.06.020
Activated Tissue-Resident Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Regulate Natural Killer Cell Immune and Tissue-Regenerative Function
Abstract
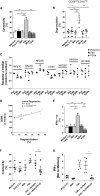
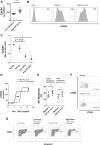
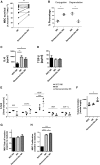
The interaction of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) with natural killer (NK) cells is traditionally thought of as a static inhibitory model, whereby resting MSCs inhibit NK cell effector function. Here, we use a dynamic in vitro system of poly(I:C) stimulation to model the interaction of NK cells and tissue-resident MSCs in the context of infection or tissue injury. The experiments suggest a time-dependent system of regulation and feedback, where, at early time points, activated MSCs secrete type I interferon to enhance NK cell effector function, while at later time points TGF-β and IL-6 limit NK cell effector function and terminate inflammatory responses by induction of a regulatory senescent-like NK cell phenotype. Importantly, feedback of these regulatory NK cells to MSCs promotes survival, proliferation, and pro-angiogenic properties. Our data provide additional insight into the interaction of stromal cells and innate immune cells and suggest a model of time-dependent MSC polarization and licensing.
Keywords: Poly(I:C); TGF-β; TLR 3; mesenchymal stromal cell polarization; mucosal tissue; natural killer cell activation; senescence; type I interferon; viral infection.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Arck P.C., Hecher K. Fetomaternal immune cross-talk and its consequences for maternal and offspring's health. Nat. Med. 2013;19:548–556. - PubMed
-
- Bernardo M.E., Fibbe W.E. Mesenchymal stromal cells: sensors and switchers of inflammation. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;13:392–402. - PubMed
-
- Cassatella M.A., Mosna F., Micheletti A., Lisi V., Tamassia N., Cont C., Calzetti F., Pelletier M., Pizzolo G., Krampera M. Toll-like receptor-3-activated human mesenchymal stromal cells significantly prolong the survival and function of neutrophils. Stem Cells. 2011;29:1001–1011. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

