Muscle Weakness in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Role of Ca2+ and Free Radical Signaling
- PMID: 28781131
- PMCID: PMC5605300
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.07.023
Muscle Weakness in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Role of Ca2+ and Free Radical Signaling
Abstract
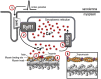
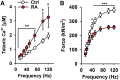
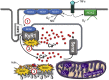
In addition to the primary symptoms arising from inflammatory processes in the joints, muscle weakness is commonly reported by patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Muscle weakness not only reduces the quality of life for the affected patients, but also dramatically increases the burden on society since patients' work ability decreases. A 25-70% reduction in muscular strength has been observed in pateints with RA when compared with age-matched healthy controls. The reduction in muscle strength is often larger than what could be explained by the reduction in muscle size in patients with RA, which indicates that intracellular (intrinsic) muscle dysfunction plays an important role in the underlying mechanism of muscle weakness associated with RA. In this review, we highlight the present understanding of RA-associated muscle weakness with special focus on how enhanced Ca2+ release from the ryanodine receptor and free radicals (reactive oxygen/nitrogen species) contributes to muscle weakness, and recent developments of novel therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: Ca(2+); Muscle weakness; Nitrosative stress; Peroxynitrite; Rheumatoid arthritis; Ryanodine receptor.
Copyright © 2017. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nitrosative modifications of the Ca2+ release complex and actin underlie arthritis-induced muscle weakness.Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Oct;74(10):1907-14. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-205007. Epub 2014 May 22. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015. PMID: 24854355 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress-induced dysregulation of excitation-contraction coupling contributes to muscle weakness.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2018 Oct;9(5):1003-1017. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12339. Epub 2018 Aug 2. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2018. PMID: 30073804 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletal muscle redox signaling in rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Sci (Lond). 2020 Nov 13;134(21):2835-2850. doi: 10.1042/CS20190728. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020. PMID: 33146370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative hotspots on actin promote skeletal muscle weakness in rheumatoid arthritis.JCI Insight. 2019 Mar 28;5(9):e126347. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.126347. JCI Insight. 2019. PMID: 30920392 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress in inflammatory cells of patient with rheumatoid arthritis: clinical efficacy of dietary antioxidants.Inflammopharmacology. 2017 Dec;25(6):595-607. doi: 10.1007/s10787-017-0397-1. Epub 2017 Sep 19. Inflammopharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28929423 Review.
Cited by
-
Maximal strength training in patients with inflammatory rheumatic disease: implications for physical function and quality of life.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2022 Jul;122(7):1671-1681. doi: 10.1007/s00421-022-04948-w. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35438424 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment with tofacitinib attenuates muscle loss through myogenin activation in the collagen-induced arthritis.Adv Rheumatol. 2024 Nov 13;64(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s42358-024-00416-5. Adv Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39538350
-
An Apriori Algorithm-Based Association Analysis of Analgesic Drugs in Chinese Medicine Prescriptions Recorded From Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain.Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 25;3:937259. doi: 10.3389/fpain.2022.937259. eCollection 2022. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35959238 Free PMC article.
-
Funcionality assessed by the core set of the international classification of functionality and health for rheumatoid arthritis: A cohort study.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 8;18(11):e0286342. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286342. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37939061 Free PMC article.
-
Biopsychosocial conditions of patients in the rheumatology department of a university hospital.Reumatologia. 2024;62(4):242-249. doi: 10.5114/reum/191793. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Reumatologia. 2024. PMID: 39381731 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alamanos Y., Voulgari P.V., Drosos A.A. Incidence and prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis, based on the 1987 American College of Rheumatology criteria: a systematic review. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;36:182–188. - PubMed
-
- Alloatti G., Penna C., Mariano F., Camussi G. Role of NO and PAF in the impairment of skeletal muscle contractility induced by TNF-alpha. Am. J. Phys. Regul. Integr. Comp. Phys. 2000;279:R2156–2163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

