The role of tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis in atherosclerosis via its two different receptors
- PMID: 28781615
- PMCID: PMC5526183
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4600
The role of tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis in atherosclerosis via its two different receptors
Abstract
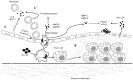
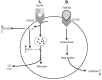
At present, it is commonly accepted that atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by disorder of the arterial wall. As one of the inflammatory cytokines of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily, tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) participates in the formation and progression of atherosclerosis. TWEAK, when binding to its initial receptor, fibroblast growth factor inducible molecule 14 (Fn14), exerts adverse biological functions in atherosclerosis, including dysfunction of endothelial cells, phenotypic change of smooth muscle cells and inflammatory responses of monocytes/macrophages. However, accumulating data supports that, besides Fn14, TWEAK also binds to cluster of differentiation (CD)163, an anti-inflammatory cytokine and a scavenger receptor exclusively expressed by monocytes and macrophages. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that CD163 is able to internalize TWEAK and likely elicits protective effects in atherosclerosis by terminating inflammation induced by TWEAK. In the present study, the role of TWEAK in atherosclerosis was reviewed, with a predominant focus on CD163 and Fn14 receptors.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; cluster of differentiation 163; fibroblast growth factor inducible molecule 14; receptor; tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A previously unrecognized protein-protein interaction between TWEAK and CD163: potential biological implications.J Immunol. 2007 Jun 15;178(12):8183-94. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.12.8183. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17548657
-
Expression of tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) and its receptor, fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 protein (Fn14), in healthy tissues and in tissues affected by periodontitis.J Periodontal Res. 2010 Aug;45(4):564-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2010.01275.x. Epub 2010 Jun 10. J Periodontal Res. 2010. PMID: 20546112
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor-Like Weak Inducer of Apoptosis (TWEAK)/Fibroblast Growth Factor-Inducible 14 (Fn14) Axis in Cardiovascular Diseases: Progress and Challenges.Cells. 2020 Feb 11;9(2):405. doi: 10.3390/cells9020405. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32053869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunohistochemical expression of tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis and fibroblast growth factor-inducible immediate early response protein 14 in oral squamous cell carcinoma and its implications.J Investig Clin Dent. 2019 Nov;10(4):e12469. doi: 10.1111/jicd.12469. Epub 2019 Sep 21. J Investig Clin Dent. 2019. PMID: 31541512
-
TWEAK and Fn14. New players in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis.Front Biosci. 2007 May 1;12:3648-55. doi: 10.2741/2341. Front Biosci. 2007. PMID: 17485328 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for posttraumatic acute respiratory distress syndrome.BMC Med Genomics. 2023 Mar 14;16(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12920-023-01482-2. BMC Med Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36918848 Free PMC article.
-
3β-Hydroxy-5β-hydroxy-B-norcholestane-6β-carboxaldehyde (SEC-B) Induces Proinflammatory Activation of Human Endothelial Cells Associated with Nitric Oxide Production and Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase/Caveolin-1 Dysregulation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jun 10;11(6):1148. doi: 10.3390/antiox11061148. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740044 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Neuroinflammation: What Role for the Tumor Necrosis Factor-Like Weak Inducer of Apoptosis/Fn14 Pathway?Front Immunol. 2017 Nov 16;8:1534. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01534. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29201025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
sTWEAK is a leukoaraiosis biomarker associated with neurovascular angiopathy.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2022 Feb;9(2):171-180. doi: 10.1002/acn3.51502. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35060359 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of CD163+ Macrophages in Inflammatory and Malignant Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 31;21(15):5497. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155497. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32752088 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Scott J. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and new opportunities for treatment and prevention. J Neural Transm Suppl. 2002:1–17. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
