Overexpression of long non-coding RNA H19 is associated with unfavorable prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer and increased proliferation and migration in colon cancer cells
- PMID: 28781681
- PMCID: PMC5530222
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.6390
Overexpression of long non-coding RNA H19 is associated with unfavorable prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer and increased proliferation and migration in colon cancer cells
Abstract
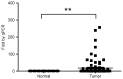
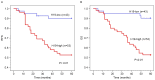
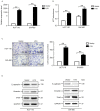
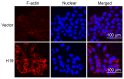
Long non-coding RNA-imprinted maternally expressed transcript (non-protein coding) (H19) has been previously identified to be involved in the development of a number of types of cancer. However, the function of H19 in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer remains unclear. The expression level of H19 in colorectal tumor tissues, and the association between H19 expression and clinicopathological variables and prognosis was investigated in the present study. In addition, the effect of H19 overexpression on viability, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of colon cancer cells was investigated in HCT-116 and SW-480 cells. The results of the present study suggest that overexpression of H19 is associated with decreased recurrence-free survival and overall survival rates in patients with colorectal cancer, and increased viability and migration in colon cancer cells. The induction of the EMT process may be an underlying molecular mechanism associated with the H19-induced increased metastasis potential of colon cancer cells.
Keywords: H19; colorectal cancer; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; metastasis; overall survival; recurrence-free survival.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Upregulation of H19 indicates a poor prognosis in gallbladder carcinoma and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Am J Cancer Res. 2015 Dec 15;6(1):15-26. eCollection 2016. Am J Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 27073719 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of long noncoding RNA H19 indicates a poor prognosis for cholangiocarcinoma and promotes cell migration and invasion by affecting epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Aug;92:17-23. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.05.061. Epub 2017 May 18. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28528181
-
The Effect of LncRNA H19/miR-194-5p Axis on the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Colorectal Adenocarcinoma.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(1):196-213. doi: 10.1159/000493968. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30278464
-
The H19 Long non-coding RNA in cancer initiation, progression and metastasis - a proposed unifying theory.Mol Cancer. 2015 Nov 4;14:184. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0458-2. Mol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26536864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNA H19 and cancer: A competing endogenous RNA.Bull Cancer. 2019 Dec;106(12):1152-1159. doi: 10.1016/j.bulcan.2019.08.011. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Bull Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31753509 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-Coding RNAs Extended Omnigenic Module of Cancers.Entropy (Basel). 2024 Jul 27;26(8):640. doi: 10.3390/e26080640. Entropy (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202109 Free PMC article.
-
Pan-cancer characterization of ncRNA synergistic competition uncovers potential carcinogenic biomarkers.PLoS Comput Biol. 2023 Oct 9;19(10):e1011308. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011308. eCollection 2023 Oct. PLoS Comput Biol. 2023. PMID: 37812646 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation analysis of serum levels of H19 and CRP levels and ulcerative colitis.J Med Biochem. 2023 Aug 25;42(3):420-426. doi: 10.5937/jomb0-41359. J Med Biochem. 2023. PMID: 37814617 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA ST3GAL6‑AS1 promotes invasion by inhibiting hnRNPA2B1‑mediated ST3GAL6 expression in multiple myeloma.Int J Oncol. 2021 Apr;58(4):5. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5185. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Int J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33649796 Free PMC article.
-
Low level of exosomal long non-coding RNA HOTTIP is a prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer.RNA Biol. 2019 Oct;16(10):1339-1345. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2019.1637697. Epub 2019 Jul 7. RNA Biol. 2019. PMID: 31251124 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
