Influence of cathode geometry on electron dynamics in an ultrafast electron microscope
- PMID: 28781982
- PMCID: PMC5515673
- DOI: 10.1063/1.4994004
Influence of cathode geometry on electron dynamics in an ultrafast electron microscope
Abstract
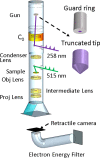
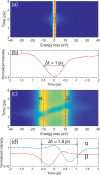
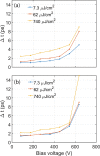
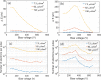
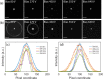
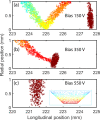
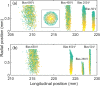
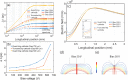
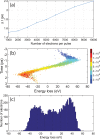
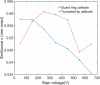
Efforts to understand matter at ever-increasing spatial and temporal resolutions have led to the development of instruments such as the ultrafast transmission electron microscope (UEM) that can capture transient processes with combined nanometer and picosecond resolutions. However, analysis by UEM is often associated with extended acquisition times, mainly due to the limitations of the electron gun. Improvements are hampered by tradeoffs in realizing combinations of the conflicting objectives for source size, emittance, and energy and temporal dispersion. Fundamentally, the performance of the gun is a function of the cathode material, the gun and cathode geometry, and the local fields. Especially shank emission from a truncated tip cathode results in severe broadening effects and therefore such electrons must be filtered by applying a Wehnelt bias. Here we study the influence of the cathode geometry and the Wehnelt bias on the performance of a photoelectron gun in a thermionic configuration. We combine experimental analysis with finite element simulations tracing the paths of individual photoelectrons in the relevant 3D geometry. Specifically, we compare the performance of guard ring cathodes with no shank emission to conventional truncated tip geometries. We find that a guard ring cathode allows operation at minimum Wehnelt bias and improve the temporal resolution under realistic operation conditions in an UEM. At low bias, the Wehnelt exhibits stronger focus for guard ring than truncated tip cathodes. The increase in temporal spread with bias is mainly a result from a decrease in the accelerating field near the cathode surface. Furthermore, simulations reveal that the temporal dispersion is also influenced by the intrinsic angular distribution in the photoemission process and the initial energy spread. However, a smaller emission spot on the cathode is not a dominant driver for enhancing time resolution. Space charge induced temporal broadening shows a close to linear relation with the number of electrons up to at least 10 000 electrons per pulse. The Wehnelt bias will affect the energy distribution by changing the Rayleigh length, and thus the interaction time, at the crossover.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influence of Photoemission Geometry on Timing and Efficiency in 4D Ultrafast Electron Microscopy.Chemphyschem. 2025 Mar 3;26(5):e202401032. doi: 10.1002/cphc.202401032. Epub 2025 Jan 28. Chemphyschem. 2025. PMID: 39804845 Free PMC article.
-
Electron beam dynamics in an ultrafast transmission electron microscope with Wehnelt electrode.Ultramicroscopy. 2016 Dec;171:8-18. doi: 10.1016/j.ultramic.2016.08.014. Epub 2016 Aug 20. Ultramicroscopy. 2016. PMID: 27584052
-
Delineation of the impact on temporal behaviors of off-axis photoemission in an ultrafast electron microscope.Rev Sci Instrum. 2024 Sep 1;95(9):093705. doi: 10.1063/5.0222993. Rev Sci Instrum. 2024. PMID: 39311672
-
4D electron microscopy: principles and applications.Acc Chem Res. 2012 Oct 16;45(10):1828-39. doi: 10.1021/ar3001684. Epub 2012 Sep 11. Acc Chem Res. 2012. PMID: 22967215
-
Photoemission sources and beam blankers for ultrafast electron microscopy.Struct Dyn. 2019 Sep 27;6(5):051501. doi: 10.1063/1.5117058. eCollection 2019 Sep. Struct Dyn. 2019. PMID: 31592440 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of a time-resolved electron microscope with a Schottky field emission gun.Struct Dyn. 2020 Oct 1;7(5):054304. doi: 10.1063/4.0000034. eCollection 2020 Sep. Struct Dyn. 2020. PMID: 33062804 Free PMC article.
-
Field Emission Air-Channel Devices as a Voltage Adder.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Nov 29;10(12):2378. doi: 10.3390/nano10122378. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33260308 Free PMC article.
-
Manipulation of Stacking Order in Td-WTe2 by Ultrafast Optical Excitation.ACS Nano. 2021 May 25;15(5):8826-8835. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c01301. Epub 2021 Apr 29. ACS Nano. 2021. PMID: 33913693 Free PMC article.
-
Time-resolved transmission electron microscopy for nanoscale chemical dynamics.Nat Rev Chem. 2023 Apr;7(4):256-272. doi: 10.1038/s41570-023-00469-y. Epub 2023 Feb 22. Nat Rev Chem. 2023. PMID: 37117417 Review.
-
Influence of Photoemission Geometry on Timing and Efficiency in 4D Ultrafast Electron Microscopy.Chemphyschem. 2025 Mar 3;26(5):e202401032. doi: 10.1002/cphc.202401032. Epub 2025 Jan 28. Chemphyschem. 2025. PMID: 39804845 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

