Phylogenetic analysis of the SINA/SIAH ubiquitin E3 ligase family in Metazoa
- PMID: 28784114
- PMCID: PMC5547486
- DOI: 10.1186/s12862-017-1024-x
Phylogenetic analysis of the SINA/SIAH ubiquitin E3 ligase family in Metazoa
Abstract
Background: The RAS signaling pathway is a pivotal developmental pathway that controls many fundamental biological processes including cell proliferation, differentiation, movement and apoptosis. Drosophila Seven-IN-Absentia (SINA) is a ubiquitin E3 ligase that is the most downstream signaling "gatekeeper" whose biological activity is essential for proper RAS signal transduction. Vertebrate SINA homologs (SIAHs) share a high degree of amino acid identity with that of Drosophila SINA. SINA/SIAH is the most conserved signaling component in the canonical EGFR/RAS/RAF/MAPK signal transduction pathway.
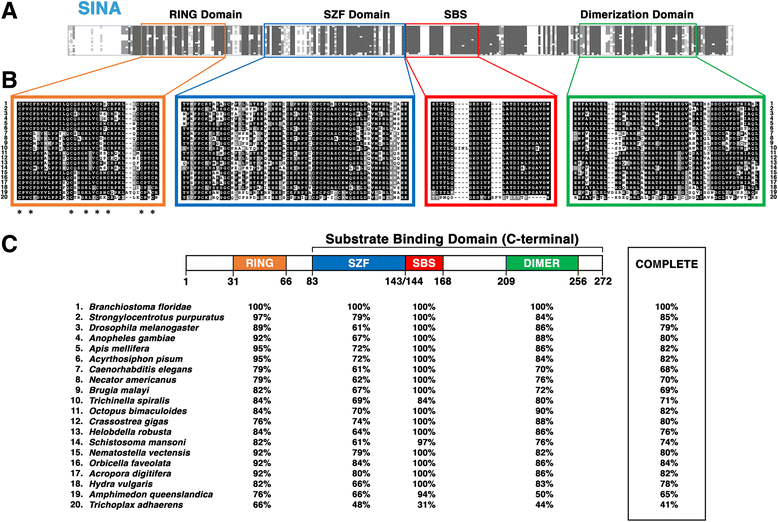
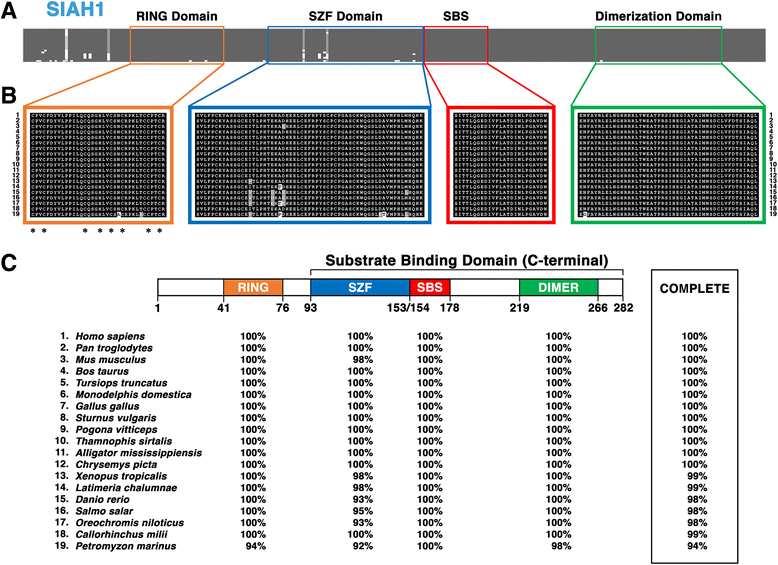
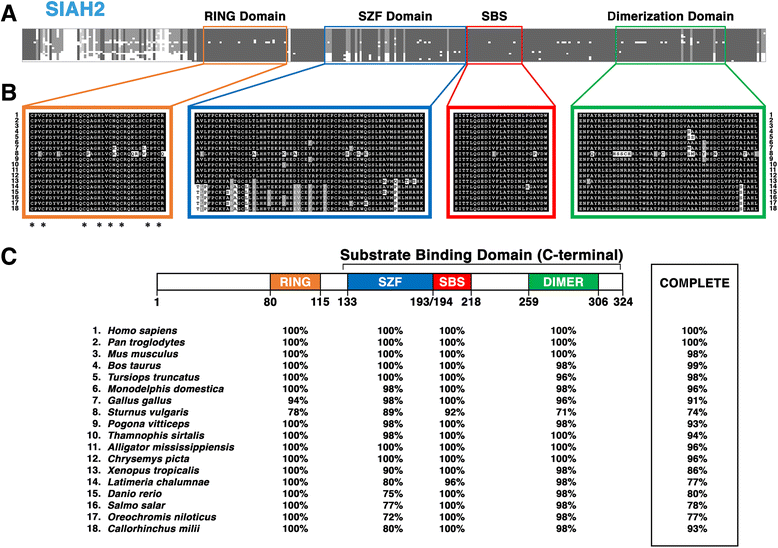
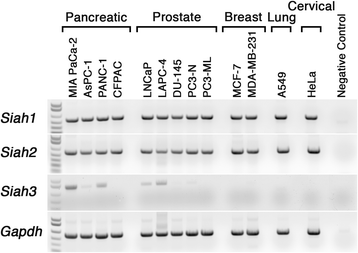
Results: Vertebrate SIAH1, 2, and 3 are the three orthologs to invertebrate SINA protein. SINA and SIAH1 orthologs are found in all major taxa of metazoans. These proteins have four conserved functional domains, known as RING (Really Interesting New Gene), SZF (SIAH-type zinc finger), SBS (substrate binding site) and DIMER (Dimerization). In addition to the siah1 gene, most vertebrates encode two additional siah genes (siah2 and siah3) in their genomes. Vertebrate SIAH2 has a highly divergent and extended N-terminal sequence, while its RING, SZF, SBS and DIMER domains maintain high amino acid identity/similarity to that of SIAH1. But unlike vertebrate SIAH1 and SIAH2, SIAH3 lacks a functional RING domain, suggesting that SIAH3 may be an inactive E3 ligase. The SIAH3 subtree exhibits a high degree of amino acid divergence when compared to the SIAH1 and SIAH2 subtrees. We find that SIAH1 and SIAH2 are expressed in all human epithelial cell lines examined thus far, while SIAH3 is only expressed in a limited subset of cancer cell lines.
Conclusion: Through phylogenetic analyses of metazoan SINA and SIAH E3 ligases, we identified many invariant and divergent amino acid residues, as well as the evolutionarily conserved functional motifs in this medically relevant gene family. Our phylomedicinal study of this unique metazoan SINA/SIAH protein family has provided invaluable evolution-based support towards future effort to design logical, potent, and durable anti-SIAH-based anticancer strategies against oncogenic K-RAS-driven metastatic human cancers. Thus, this method of evolutionary study should be of interest in cancer biology.
Keywords: And conserved functional domains in SINA; Invariant and divergent amino acid residues; Phylogenetic analysis; RAS signal transduction; SIAH1; SIAH2 and SIAH3; SINA/SIAH E3 ligases; Ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable. All metazoan SINA/SIAH sequences are publically available at GenBank and NCBI. Human cancer cell lines were purchased from ATCC. No patient information was used in this study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The substrate binding domains of human SIAH E3 ubiquitin ligases are now crystal clear.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017 Jan;1861(1 Pt A):3095-3105. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.10.019. Epub 2016 Oct 21. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017. PMID: 27776223
-
RING dimerisation drives higher-order organisation of SINA/SIAH E3 ubiquitin ligases.FEBS J. 2025 Jun;292(11):2784-2805. doi: 10.1111/febs.70000. Epub 2025 Feb 5. FEBS J. 2025. PMID: 39910688
-
Characterization of human homologs of the Drosophila seven in absentia (sina) gene.Genomics. 1997 Nov 15;46(1):103-11. doi: 10.1006/geno.1997.4997. Genomics. 1997. PMID: 9403064
-
A New Strategy to Control and Eradicate "Undruggable" Oncogenic K-RAS-Driven Pancreatic Cancer: Molecular Insights and Core Principles Learned from Developmental and Evolutionary Biology.Cancers (Basel). 2018 May 14;10(5):142. doi: 10.3390/cancers10050142. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29757973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The inducible E3 ubiquitin ligases SIAH1 and SIAH2 perform critical roles in breast and prostate cancers.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015 Aug;26(4):405-13. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2015.04.002. Epub 2015 May 12. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015. PMID: 26028498 Review.
Cited by
-
Rice SIAH E3 Ligases Interact with RMD Formin and Affect Plant Morphology.Rice (N Y). 2022 Jan 25;15(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12284-022-00554-8. Rice (N Y). 2022. PMID: 35075530 Free PMC article.
-
Zooming into the structure-function of RING finger proteins for anti-cancer therapeutic applications.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Jul 15;13(7):2773-2789. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37559981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene Expression Profiling of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells in Hypercapnia Identifies SIAH3 as a Novel Prognostic Biomarker.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 21;26(7):2848. doi: 10.3390/ijms26072848. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243415 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent EGFR/K-RAS/SIAH pathway activation drives chemo-resistance and early tumor relapse in triple-negative breast cancer.Cancer Drug Resist. 2022 Jun 22;5(3):691-702. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2022.31. eCollection 2022. Cancer Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 36176751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of the SIAH2-HIF-1 Axis by Protein Kinases and Its Implication in Cancer Therapy.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 25;9:646687. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.646687. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33842469 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

