Detecting and characterizing mixed infections with genetic variants of Anaplasma phagocytophilum in roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) by developing an ankA cluster-specific nested PCR
- PMID: 28784148
- PMCID: PMC5547487
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-017-2316-0
Detecting and characterizing mixed infections with genetic variants of Anaplasma phagocytophilum in roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) by developing an ankA cluster-specific nested PCR
Abstract
Background: Anaplasma phagocytophilum is a tick-transmitted Gram-negative obligate intracellular bacterium able to infect a wide variety of wild and domestic animals worldwide. Based on the genetic diversity observed with different molecular markers, several host-specific lineages have been identified. Roe deer is one of the most important reservoirs of this bacterium and hosts different genetic groups sometimes found on domestic animals. We therefore developed an ankA cluster-specific nested PCR (nPCR) to evaluate the prevalence of the three different ankA genetic groups described in roe deer (clusters II, III and IV) at three locations in France and the level of co-infections.
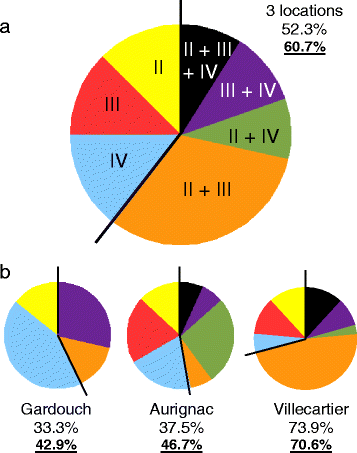
Results: The specificity of the three nPCRs was assessed by partially sequencing 35 amplicons of ankA genes obtained from the different nested PCRs. All three genetic lineages were detected in roe deer from all three geographical locations. Of the infected deer population, 60.7% were co-infected by two or three different genetic variants. Co-infections varied from 42.9 to 70.6% of the infected population depending on the local infection prevalences (from 33.3 to 73.9%). All types of mixed infections occurred, suggesting the absence of a strict variant exclusion by another variant.
Conclusions: Mixed infections by two or three genetic variants of A. phagocytopilum are a common feature in roe deer. Genetic variants (cluster IV) also found in domestic ruminants (cattle and sheep) were present in all the roe deer populations analyzed, suggesting a shared epidemiological cycle.
Keywords: Anaplasma phagocytophilum; Capreolus capreolus; Co-infection; France; Nested polymerase chain reaction; Reservoir; Tick-borne diseases; ankA variant.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Dumler JS, Barbet AF, Bekker CP, Dasch GA, Palmer GH, Ray SC, et al. Reorganization of genera in the families Rickettsiaceae and Anaplasmataceae in the order Rickettsiales: unification of some species of Ehrlichia with Anaplasma, Cowdria with Ehrlichia and Ehrlichia with Neorickettsia, descriptions of six new species combinations and designation of Ehrlichia equi and ‘HGE agent’ as subjective synonyms of Ehrlichia phagocytophila. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2001;51:2145–2165. doi: 10.1099/00207713-51-6-2145. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rar V, Golovljova I. Anaplasma, Ehrlichia, and “Candidatus Neoehrlichia” bacteria: pathogenicity, biodiversity, and molecular genetic characteristics, a review. Infect Genet Evol. 2011;11(8):1842–61. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

