Large-scale 3-dimensional quantitative imaging of tissues: state-of-the-art and translational implications
- PMID: 28784428
- PMCID: PMC5659947
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trsl.2017.07.006
Large-scale 3-dimensional quantitative imaging of tissues: state-of-the-art and translational implications
Abstract
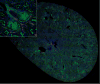
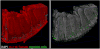
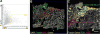
Recent developments in automated optical sectioning microscope systems have enabled researchers to conduct high resolution, three-dimensional (3D) microscopy at the scale of millimeters in various types of tissues. This powerful technology allows the exploration of tissues at an unprecedented level of detail, while preserving the spatial context. By doing so, such technology will also enable researchers to explore cellular and molecular signatures within tissue and correlate with disease course. This will allow an improved understanding of pathophysiology and facilitate a precision medicine approach to assess the response to treatment. The ability to perform large-scale imaging in 3D cannot be realized without the widespread availability of accessible quantitative analysis. In this review, we will outline recent advances in large-scale 3D imaging and discuss the available methodologies to perform meaningful analysis and potential applications in translational research.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
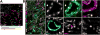


References
-
- Furness PN, Philpott CM, Chorbadjian MT, Nicholson ML, Bosmans JL, Corthouts BL, et al. Protocol biopsy of the stable renal transplant: a multicenter study of methods and complication rates. Transplantation. 2003;76:969–73. - PubMed
-
- Hiemann NE, Wellnhofer E, Knosalla C, Lehmkuhl HB, Stein J, Hetzer R, et al. Prognostic impact of microvasculopathy on survival after heart transplantation: evidence from 9713 endomyocardial biopsies. Circulation. 2007;116:1274–82. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett JM, Brookes CL, Robson T, van de Velde CJ, Billingham LJ, Campbell FM, et al. Estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor as predictive biomarkers of response to endocrine therapy: a prospectively powered pathology study in the Tamoxifen and Exemestane Adjuvant Multinational trial. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:1531–8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Harvey JM, Clark GM, Osborne CK, Allred DC. Estrogen receptor status by immunohistochemistry is superior to the ligand-binding assay for predicting response to adjuvant endocrine therapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:1474–81. - PubMed
-
- Harris L, Fritsche H, Mennel R, Norton L, Ravdin P, Taube S, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology 2007 update of recommendations for the use of tumor markers in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:5287–312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

