Efficient reduction of CO2 by the molybdenum-containing formate dehydrogenase from Cupriavidus necator (Ralstonia eutropha)
- PMID: 28784661
- PMCID: PMC5641872
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.785576
Efficient reduction of CO2 by the molybdenum-containing formate dehydrogenase from Cupriavidus necator (Ralstonia eutropha)
Abstract
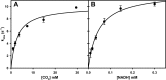
The ability of the FdsABG formate dehydrogenase from Cupriavidus necator (formerly known as Ralstonia eutropha) to catalyze the reverse of the physiological reaction, the reduction of CO2 to formate utilizing NADH as electron donor, has been investigated. Contrary to previous studies of this enzyme, we demonstrate that it is in fact effective in catalyzing the reverse reaction with a kcat of 11 ± 0.4 s-1 We also quantify the stoichiometric accumulation of formic acid as the product of the reaction and demonstrate that the observed kinetic parameters for catalysis in the forward and reverse reactions are thermodynamically consistent, complying with the expected Haldane relationships. Finally, we demonstrate the reaction conditions necessary for gauging the ability of a given formate dehydrogenase or other CO2-utilizing enzyme to catalyze the reverse direction to avoid false negative results. In conjunction with our earlier studies on the reaction mechanism of this enzyme and on the basis of the present work, we conclude that all molybdenum- and tungsten-containing formate dehydrogenases and related enzymes likely operate via a simple hydride transfer mechanism and are effective in catalyzing the reversible interconversion of CO2 and formate under the appropriate experimental conditions.
Keywords: biofuel; carbon dioxide; enzyme catalysis; molybdenum; multifunctional enzyme.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures





References
-
- Maia L. B., Moura J. J., and Moura I. (2015) Molybdenum and tungsten-dependent formate dehydrogenases. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 20, 287–309 - PubMed
-
- Sun Q., Jiang Y., Jiang Z., Zhang L., Sun X., and Li J. (2009) Green and efficient conversion of CO2 to methanol by biomimetic coimmobilization of three dehydrogenases in protamine-templated titania. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 48, 4210–4215
-
- Olah G. A. (2005) Beyond oil and gas: the methanol economy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 44, 2636–2639 - PubMed
-
- Qiao J., Liu Y., Hong F., and Zhang J. (2014) A review of catalysts for the electroreduction of carbon dioxide to produce low-carbon fuels. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 631–675 - PubMed
-
- Maia L. B., Moura I., and Moura J. J. G. (2017) Molybdenum and tungsten-containing formate dehydrogenases: aiming to inspire a catalyst for carbon dioxide utilization. Inorg. Chim. Acta 455, 350–363
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

