Mechanism of DNA alkylation-induced transcriptional stalling, lesion bypass, and mutagenesis
- PMID: 28784758
- PMCID: PMC5576830
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1708748114
Mechanism of DNA alkylation-induced transcriptional stalling, lesion bypass, and mutagenesis
Abstract
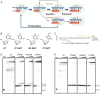
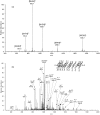
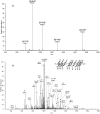
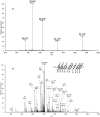
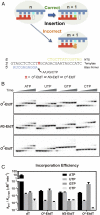
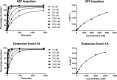
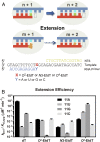
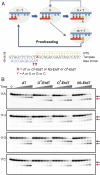
Alkylated DNA lesions, induced by both exogenous chemical agents and endogenous metabolites, interfere with the efficiency and accuracy of DNA replication and transcription. However, the molecular mechanisms of DNA alkylation-induced transcriptional stalling and mutagenesis remain unknown. In this study, we systematically investigated how RNA polymerase II (pol II) recognizes and bypasses regioisomeric O2-, N3-, and O4-ethylthymidine (O2-, N3-, and O4-EtdT) lesions. We observed distinct pol II stalling profiles for the three regioisomeric EtdT lesions. Intriguingly, pol II stalling at O2-EtdT and N3-EtdT sites is exacerbated by TFIIS-stimulated proofreading activity. Assessment for the impact of the EtdT lesions on individual fidelity checkpoints provided further mechanistic insights, where the transcriptional lesion bypass routes for the three EtdT lesions are controlled by distinct fidelity checkpoints. The error-free transcriptional lesion bypass route is strongly favored for the minor-groove O2-EtdT lesion. In contrast, a dominant error-prone route stemming from GMP misincorporation was observed for the major-groove O4-EtdT lesion. For the N3-EtdT lesion that disrupts base pairing, multiple transcriptional lesion bypass routes were found. Importantly, the results from the present in vitro transcriptional studies are well correlated with in vivo transcriptional mutagenesis analysis. Finally, we identified a minor-groove-sensing motif from pol II (termed Pro-Gate loop). The Pro-Gate loop faces toward the minor groove of RNA:DNA hybrid and is involved in modulating the translocation of minor-groove alkylated DNA template after nucleotide incorporation opposite the lesion. Taken together, this work provides important mechanistic insights into transcriptional stalling, lesion bypass, and mutagenesis of alkylated DNA lesions.
Keywords: DNA alkylation; RNA polymerase II; transcription; transcriptional lesion bypass; transcriptional mutagenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Transcriptional bypass of regioisomeric ethylated thymidine lesions by T7 RNA polymerase and human RNA polymerase II.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Dec 16;42(22):13706-13. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1183. Epub 2014 Nov 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25404131 Free PMC article.
-
Replication across regioisomeric ethylated thymidine lesions by purified DNA polymerases.Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Nov 18;26(11):1730-8. doi: 10.1021/tx4002995. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 24134187 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxic and mutagenic properties of regioisomeric O²-, N3- and O⁴-ethylthymidines in bacterial cells.Carcinogenesis. 2014 Sep;35(9):2002-6. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgu085. Epub 2014 Apr 7. Carcinogenesis. 2014. PMID: 24710626 Free PMC article.
-
Mass Spectrometry-Based Quantitative Strategies for Assessing the Biological Consequences and Repair of DNA Adducts.Acc Chem Res. 2016 Feb 16;49(2):205-13. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00437. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Acc Chem Res. 2016. PMID: 26758048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular basis of transcriptional fidelity and DNA lesion-induced transcriptional mutagenesis.DNA Repair (Amst). 2014 Jul;19:71-83. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2014.03.024. Epub 2014 Apr 21. DNA Repair (Amst). 2014. PMID: 24767259 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Causes and consequences of DNA double-stranded breaks in cardiovascular disease.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Apr;480(4):2043-2064. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05131-9. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39404936 Review.
-
RNA polymerase II stalls on oxidative DNA damage via a torsion-latch mechanism involving lone pair-π and CH-π interactions.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Apr 28;117(17):9338-9348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1919904117. Epub 2020 Apr 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32284409 Free PMC article.
-
A unified Watson-Crick geometry drives transcription of six-letter expanded DNA alphabets by E. coli RNA polymerase.Nat Commun. 2023 Dec 12;14(1):8219. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43735-9. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38086811 Free PMC article.
-
A chemical method for generating live-attenuated, replication-defective DNA viruses for vaccine development.Cell Rep Methods. 2022 Sep 8;2(9):100287. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2022.100287. eCollection 2022 Sep 19. Cell Rep Methods. 2022. PMID: 36160049 Free PMC article.
-
Human DNA Mutations and their Impact on Genetic Disorders.Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2024;18(4):288-315. doi: 10.2174/0118722083255081231020055309. Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37936448 Review.
References
-
- Ljungman M, Lane DP. Transcription—guarding the genome by sensing DNA damage. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:727–737. - PubMed
-
- Tornaletti S, Hanawalt PC. Effect of DNA lesions on transcription elongation. Biochimie. 1999;81:139–146. - PubMed
-
- Saxowsky TT, Doetsch PW. RNA polymerase encounters with DNA damage: Transcription-coupled repair or transcriptional mutagenesis? Chem Rev. 2006;106:474–488. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

