Mechanism of DNA alkylation-induced transcriptional stalling, lesion bypass, and mutagenesis
- PMID: 28784758
- PMCID: PMC5576830
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1708748114
Mechanism of DNA alkylation-induced transcriptional stalling, lesion bypass, and mutagenesis
Abstract
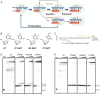
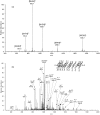
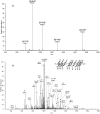
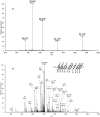
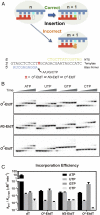
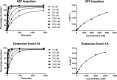
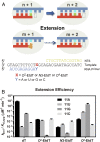
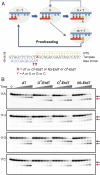
Alkylated DNA lesions, induced by both exogenous chemical agents and endogenous metabolites, interfere with the efficiency and accuracy of DNA replication and transcription. However, the molecular mechanisms of DNA alkylation-induced transcriptional stalling and mutagenesis remain unknown. In this study, we systematically investigated how RNA polymerase II (pol II) recognizes and bypasses regioisomeric O2-, N3-, and O4-ethylthymidine (O2-, N3-, and O4-EtdT) lesions. We observed distinct pol II stalling profiles for the three regioisomeric EtdT lesions. Intriguingly, pol II stalling at O2-EtdT and N3-EtdT sites is exacerbated by TFIIS-stimulated proofreading activity. Assessment for the impact of the EtdT lesions on individual fidelity checkpoints provided further mechanistic insights, where the transcriptional lesion bypass routes for the three EtdT lesions are controlled by distinct fidelity checkpoints. The error-free transcriptional lesion bypass route is strongly favored for the minor-groove O2-EtdT lesion. In contrast, a dominant error-prone route stemming from GMP misincorporation was observed for the major-groove O4-EtdT lesion. For the N3-EtdT lesion that disrupts base pairing, multiple transcriptional lesion bypass routes were found. Importantly, the results from the present in vitro transcriptional studies are well correlated with in vivo transcriptional mutagenesis analysis. Finally, we identified a minor-groove-sensing motif from pol II (termed Pro-Gate loop). The Pro-Gate loop faces toward the minor groove of RNA:DNA hybrid and is involved in modulating the translocation of minor-groove alkylated DNA template after nucleotide incorporation opposite the lesion. Taken together, this work provides important mechanistic insights into transcriptional stalling, lesion bypass, and mutagenesis of alkylated DNA lesions.
Keywords: DNA alkylation; RNA polymerase II; transcription; transcriptional lesion bypass; transcriptional mutagenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


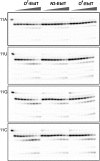
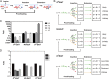


References
-
- Ljungman M, Lane DP. Transcription—guarding the genome by sensing DNA damage. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:727–737. - PubMed
-
- Tornaletti S, Hanawalt PC. Effect of DNA lesions on transcription elongation. Biochimie. 1999;81:139–146. - PubMed
-
- Saxowsky TT, Doetsch PW. RNA polymerase encounters with DNA damage: Transcription-coupled repair or transcriptional mutagenesis? Chem Rev. 2006;106:474–488. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

