Phosphoserine Phosphatase Is Required for Serine and One-Carbon Unit Synthesis in Hydrogenobacter thermophilus
- PMID: 28784815
- PMCID: PMC5626962
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00409-17
Phosphoserine Phosphatase Is Required for Serine and One-Carbon Unit Synthesis in Hydrogenobacter thermophilus
Abstract
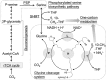
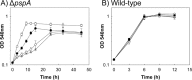
Hydrogenobacter thermophilus is an obligate chemolithoautotrophic bacterium of the phylum Aquificae and is capable of fixing carbon dioxide through the reductive tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. The recent discovery of two novel-type phosphoserine phosphatases (PSPs) in H. thermophilus suggests the presence of a phosphorylated serine biosynthesis pathway; however, the physiological role of these novel-type metal-independent PSPs (iPSPs) in H. thermophilus has not been confirmed. In the present study, a mutant strain with a deletion of pspA, the catalytic subunit of iPSPs, was constructed and characterized. The generated mutant was a serine auxotroph, suggesting that the novel-type PSPs and phosphorylated serine synthesis pathway are essential for serine anabolism in H. thermophilus. As an autotrophic medium supplemented with glycine did not support the growth of the mutant, the reversible enzyme serine hydroxymethyltransferase does not appear to synthesize serine from glycine and may therefore generate glycine and 5,10-CH2-tetrahydrofolate (5,10-CH2-THF) from serine. This speculation is supported by the lack of glycine cleavage activity, which is needed to generate 5,10-CH2-THF, in H. thermophilus Determining the mechanism of 5,10-CH2-THF synthesis is important for understanding the fundamental anabolic pathways of organisms, because 5,10-CH2-THF is a major one-carbon donor that is used for the synthesis of various essential compounds, including nucleic and amino acids. The findings from the present experiments using a pspA deletion mutant have confirmed the physiological role of iPSPs as serine producers and show that serine is a major donor of one-carbon units in H. thermophilusIMPORTANCE Serine biosynthesis and catabolism pathways are intimately related to the metabolism of 5,10-CH2-THF, a one-carbon donor that is utilized for the biosynthesis of various essential compounds. For this reason, determining the mechanism of serine synthesis is important for understanding the fundamental anabolic pathways of microorganisms. In the present study, we experimentally confirmed that a novel phosphoserine phosphatase in the obligate chemolithoautotrophic bacterium Hydrogenobacter thermophilus is essential for serine biosynthesis. This finding indicates that serine is synthesized from an intermediate of gluconeogenesis in H. thermophilus In addition, because glycine cleavage system activity and genes encoding an enzyme capable of producing 5,10-CH2-THF were not detected, serine appears to be the major one-carbon donor to tetrahydrofolate (THF) in H. thermophilus.
Keywords: amino acid biosynthesis; carbon metabolism; thermophiles.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structural units important for activity of a novel-type phosphoserine phosphatase from Hydrogenobacter thermophilus TK-6 revealed by crystal structure analysis.J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 19;288(16):11448-58. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.449561. Epub 2013 Mar 11. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23479726 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and analysis of cofactor-dependent phosphoglycerate mutase homologs as novel phosphoserine phosphatases in Hydrogenobacter thermophilus.J Biol Chem. 2012 Apr 6;287(15):11934-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.330621. Epub 2012 Feb 15. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22337887 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and analysis of a novel type of the serine biosynthetic enzyme phosphoserine phosphatase in Thermus thermophilus.FEBS J. 2019 Feb;286(4):726-736. doi: 10.1111/febs.14703. Epub 2018 Dec 7. FEBS J. 2019. PMID: 30430741
-
Molecular biology of the plastidic phosphorylated serine biosynthetic pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana.Amino Acids. 2001;20(3):243-59. doi: 10.1007/s007260170042. Amino Acids. 2001. PMID: 11354602 Review.
-
Novel enzyme reactions related to the tricarboxylic acid cycle: phylogenetic/functional implications and biotechnological applications.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007 May;75(2):249-55. doi: 10.1007/s00253-007-0893-0. Epub 2007 Feb 28. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17333169 Review.
Cited by
-
Heterologous gene expression and characterization of two serine hydroxymethyltransferases from Thermoplasma acidophilum.Extremophiles. 2021 Jul;25(4):393-402. doi: 10.1007/s00792-021-01238-9. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Extremophiles. 2021. PMID: 34196829
-
Comparative analysis of bacterial diversity in two hot springs in Hefei, China.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 10;13(1):5832. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-32853-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37037855 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon Fixation in the Chemolithoautotrophic Bacterium Aquifex aeolicus Involves Two Low-Potential Ferredoxins as Partners of the PFOR and OGOR Enzymes.Life (Basel). 2023 Feb 23;13(3):627. doi: 10.3390/life13030627. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36983784 Free PMC article.
-
The Properties of 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate Dehydrogenase (MetF1) and Its Role in the Tetrahydrofolate-Dependent Dicamba Demethylation System in Rhizorhabdus dicambivorans Ndbn-20.J Bacteriol. 2019 Aug 8;201(17):e00096-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00096-19. Print 2019 Sep 1. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 31209079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shiba H, Kawasumi T, Igarashi Y, Kodama T, Minoda Y. 1985. The CO2 assimilation via the reductive tricarboxylic acid cycle in an obligately autotrophic, aerobic hydrogen-oxidizing bacterium, Hydrogenobacter thermophilus. Arch Microbiol 141:198–203. doi:10.1007/BF00408058. - DOI
-
- Shiba H, Kawasumi T, Igarashi Y, Kodama T, Minoda Y. 1982. The deficient carbohydrate metabolic pathways and the incomplete tricarboxylic acid cycle in an obligately autotrophic hydrogen-oxidizing bacterium. Agric Biol Chem 46:2341–2345. doi:10.1080/00021369.1982.10865433. - DOI
-
- Chiba Y, Horita S, Ohtsuka J, Arai H, Nagata K, Igarashi Y, Tanokura M, Ishii M. 2013. Structural units important for activity of a novel-type phosphoserine phosphatase from Hydrogenobacter thermophilus TK-6 revealed by crystal structure analysis. J Biol Chem 288:11448–11458. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.449561. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

