p38α: A Profibrotic Signaling Nexus
- PMID: 28784825
- PMCID: PMC5709048
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.028957
p38α: A Profibrotic Signaling Nexus
Keywords: Editorials; fibrosis; heart; inhibitor; kinase; myofibroblast.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
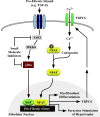
Comment on
-
Fibroblast-Specific Genetic Manipulation of p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase In Vivo Reveals Its Central Regulatory Role in Fibrosis.Circulation. 2017 Aug 8;136(6):549-561. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.026238. Epub 2017 Mar 29. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 28356446 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shah RV, Desai AS, Givertz MM. The effect of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors on mortality and heart failure hospitalization in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Card Fail. 2010;16:260–267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

