Use of Proteomics To Investigate Kidney Function Decline over 5 Years
- PMID: 28784837
- PMCID: PMC5544512
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.08780816
Use of Proteomics To Investigate Kidney Function Decline over 5 Years
Abstract
Background and objectives: Using a discovery/replication approach, we investigated associations between a multiplex panel of 80 circulating proteins associated with cardiovascular pathology or inflammation, and eGFR decline per year and CKD incidence.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: We used two cohorts, the Prospective Investigation of the Vasculature in Uppsala Seniors Study (PIVUS; n=687, mean age of 70 years, 51% women) and the Uppsala Longitudinal Study of Adult Men (ULSAM; n=360 men, mean age of 78 years), with 5-year follow-up data on eGFR. There were 231 and 206 incident cases of CKD during follow-up in the PIVUS and ULSAM studies, respectively. Proteomic profiling of 80 proteins was assessed by a multiplex assay (proximity extension assay). The assay uses two antibodies for each protein and a PCR step to achieve a high-specific binding and the possibility to measure multiple proteins in parallel, but gives no absolute concentrations.
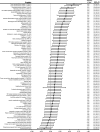
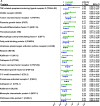
Results: In the discovery cohort from the PIVUS Study, 28 plasma proteins were significantly associated with eGFR decline per year, taking into account the multiple testing. Twenty of these proteins were significantly associated with eGFR decline per year in the replication cohort from the ULSAM Study after adjustment for age, sex, cardiovascular risk factors, medications, and urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (in order of significance: TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor 2*, CD40L receptor, TNF receptor 1*, placenta growth factor*, thrombomodulin*, urokinase plasminogen activator surface receptor*, growth/differentiation factor 15*, macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1, fatty acid-binding protein*, cathepsin D, resistin, kallikrein 11*, C-C motif chemokine 3, proteinase-activated receptor 1*, cathepsin L, chitinase 3-like protein 1, TNF receptor 2*, fibroblast growth factor 23*, monocyte chemotactic protein 1, and kallikrein 6). Moreover, 11 of the proteins predicted CKD incidence (marked with * above). No protein consistently predicted eGFR decline per year independently of baseline eGFR in both cohorts.
Conclusions: Several circulating proteins involved in phosphate homeostasis, inflammation, apoptosis, extracellular matrix remodeling, angiogenesis, and endothelial dysfunction were associated with worsening kidney function. Multiplex proteomics appears to be a promising way of discovering novel aspects of kidney disease pathology.
Keywords: Adult; Aged; Albumins; Cardiovascular Diseases; Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins; Fibroblast Growth Factors; Follow-Up Studies; Homeostasis; Longitudinal Studies; Phosphates; Plasminogen; Prospective Studies; Proteomics; Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator; apoptosis; creatinine; extracellular matrix; glomerular filtration rate; risk factors.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures


Comment in
-
The Possibilities to Improve Kidney Health with Proteomics.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Aug 7;12(8):1206-1208. doi: 10.2215/CJN.06200617. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28733352 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Eckardt KU, Coresh J, Devuyst O, Johnson RJ, Köttgen A, Levey AS, Levin A: Evolving importance of kidney disease: From subspecialty to global health burden. Lancet 382: 158–169, 2013 - PubMed
-
- Coresh J, Turin TC, Matsushita K, Sang Y, Ballew SH, Appel LJ, Arima H, Chadban SJ, Cirillo M, Djurdjev O, Green JA, Heine GH, Inker LA, Irie F, Ishani A, Ix JH, Kovesdy CP, Marks A, Ohkubo T, Shalev V, Shankar A, Wen CP, de Jong PE, Iseki K, Stengel B, Gansevoort RT, Levey AS; CKD Prognosis Consortium : Decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate and subsequent risk of end-stage renal disease and mortality. JAMA 311: 2518–2531, 2014 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Holzmann MJ, Aastveit A, Hammar N, Jungner I, Walldius G, Holme I: Renal dysfunction increases the risk of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke in the general population. Ann Med 44: 607–615, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Matsushita K, Mahmoodi BK, Woodward M, Emberson JR, Jafar TH, Jee SH, Polkinghorne KR, Shankar A, Smith DH, Tonelli M, Warnock DG, Wen CP, Coresh J, Gansevoort RT, Hemmelgarn BR, Levey AS; Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis Consortium : Comparison of risk prediction using the CKD-EPI equation and the MDRD study equation for estimated glomerular filtration rate. JAMA 307: 1941–1951, 2012 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Matsushita K, van der Velde M, Astor BC, Woodward M, Levey AS, de Jong PE, Coresh J, Gansevoort RT; Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis Consortium : Association of estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in general population cohorts: A collaborative meta-analysis. Lancet 375: 2073–2081, 2010 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

