Inhibition of PAI-1 Activity by Toddalolactone as a Mechanism for Promoting Blood Circulation and Removing Stasis by Chinese Herb Zanthoxylum nitidum var. tomentosum
- PMID: 28785222
- PMCID: PMC5519579
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00489
Inhibition of PAI-1 Activity by Toddalolactone as a Mechanism for Promoting Blood Circulation and Removing Stasis by Chinese Herb Zanthoxylum nitidum var. tomentosum
Abstract
Traditional Chinese medicine has been used to treat a variety of human diseases for many centuries. Zanthoxylum nitidum var. tomentosum is used as an adjuvant to promote blood circulation and remove stasis. However, the mechanisms of improving circulation and other biological activities of Z. nitidum var. tomentosum are still unclear. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) regulates the plasminogen activation system through inhibition of tissue-type and urokinase-type plasminogen activators (tPA and uPA). PAI-1 has been linked to fibrin deposition that evolves into organ fibrosis and atherosclerosis. In the present study, we showed that ethanol extract prepared from Z. nitidum var. tomentosum exhibited PAI-1 inhibitory activity, and identified toddalolactone as the main active component that inhibited the activity of recombinant human PAI-1 with IC50 value of 37.31 ± 3.23 μM, as determined by chromogenic assay, and the effect was further confirmed by clot lysis assay. In vitro study showed that toddalolactone inhibited the binding between PAI-1 and uPA, and therefore prevented the formation of the PAI-1/uPA complex. Intraperitoneal injection of toddalolactone in mice significantly prolonged tail bleeding and reduced arterial thrombus weight in a FeCl3-induced thrombosis model. In addition, the hydroxyproline level in the plasma and the degree of liver fibrosis in mice were decreased after intraperitoneal injection of toddalolactone in CCl4-induced mouse liver fibrosis model. Taken together, PAI-1 inhibition exerted by toddalolactone may represent a novel molecular mechanism by which Z. nitidum var. tomentosum manifests its effect in the treatment of thrombosis and fibrosis.
Keywords: PAI-1; PAI-1 inhibitor; fibrinolysis; pharmacology; toddalolactone.
Figures
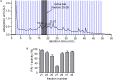


 ) or with 30 μM (
) or with 30 μM ( ), 60 μM (
), 60 μM ( ), 125 μM (
), 125 μM ( ), 250 μM (
), 250 μM ( ) and 500 μM (
) and 500 μM ( ) of toddalolactone, or by uPA only (
) of toddalolactone, or by uPA only ( ). (D) Effect of toddalolactone on uPA activity in the presence of PAI-1. Data are the means ± SEs from five experiments, each carried out in duplicate. “∗” and “∗∗” indicate significantly different from the control (no toddalolactone) at the P < 0.05 and P < 0.01 level, respectively.
). (D) Effect of toddalolactone on uPA activity in the presence of PAI-1. Data are the means ± SEs from five experiments, each carried out in duplicate. “∗” and “∗∗” indicate significantly different from the control (no toddalolactone) at the P < 0.05 and P < 0.01 level, respectively.

Similar articles
-
Bioactivity-Guided Fractionation of the Traditional Chinese Medicine Resina Draconis Reveals Loureirin B as a PAI-1 Inhibitor.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:9425963. doi: 10.1155/2017/9425963. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 29234445 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) by the naphthoquinone shikonin.Fitoterapia. 2016 Sep;113:117-22. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2016.07.010. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Fitoterapia. 2016. PMID: 27476618
-
A long-acting PAI-1 inhibitor reduces thrombus formation.Thromb Haemost. 2017 Jun 28;117(7):1338-1347. doi: 10.1160/TH16-11-0891. Epub 2017 Apr 13. Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 28405670
-
Coagulation, fibrinolysis, and fibrin deposition in acute lung injury.Crit Care Med. 2003 Apr;31(4 Suppl):S213-20. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000057846.21303.AB. Crit Care Med. 2003. PMID: 12682443 Review.
-
Inhibition of PAI-1: a new anti-thrombotic approach.Curr Drug Targets Cardiovasc Haematol Disord. 2002 Jun;2(1):27-42. doi: 10.2174/1568006023337727. Curr Drug Targets Cardiovasc Haematol Disord. 2002. PMID: 12769655 Review.
Cited by
-
Six Express Sequence Tag-Simple Sequence Repeat Primers Reveal Genetic Diversity in the Cultivars of Three Zanthoxylum Species.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Aug 30;45(9):7183-7196. doi: 10.3390/cimb45090454. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37754238 Free PMC article.
-
Zanthoxylum Species: A Comprehensive Review of Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, Pharmacological and Nutraceutical Applications.Molecules. 2021 Jun 30;26(13):4023. doi: 10.3390/molecules26134023. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34209371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sesquiterpenoids from the Florets of Carthamus tinctorius (Safflower) and Their Anti-Atherosclerotic Activity.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 16;14(24):5348. doi: 10.3390/nu14245348. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36558507 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro differences in toddalolactone metabolism in various species and its effect on cytochrome P450 expression.Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):1591-1605. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2108062. Pharm Biol. 2022. PMID: 35944298 Free PMC article.
-
Toddalolactone protects against osteoarthritis by ameliorating chondrocyte inflammation and suppressing osteoclastogenesis.Chin Med. 2022 Feb 5;17(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s13020-022-00576-w. Chin Med. 2022. PMID: 35123541 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bollen L., Vande Casteele N., Peeters M., Bessonov K., Van Steen K., Rutgeerts P., et al. (2015). Short-term effect of infliximab is reflected in the clot lysis profile of patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a prospective study. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 21 570–578. 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000301 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

