Estimation of smooth ROC curves for biomarkers with limits of detection
- PMID: 28786136
- PMCID: PMC5679135
- DOI: 10.1002/sim.7394
Estimation of smooth ROC curves for biomarkers with limits of detection
Abstract
Protein biomarkers found in plasma are commonly used for cancer screening and early detection. Measurements obtained by such markers are often based on different assays that may not support detection of accurate measurements due to a limit of detection. The ROC curve is the most popular statistical tool for the evaluation of a continuous biomarker. However, in situations where limits of detection exist, the empirical ROC curve fails to provide a valid estimate for the whole spectrum of the false positive rate (FPR). Hence, crucial information regarding the performance of the marker in high sensitivity and/or high specificity values is not revealed. In this paper, we address this problem and propose methods for constructing ROC curve estimates for all possible FPR values. We explore flexible parametric methods, transformations to normality, and robust kernel-based and spline-based approaches. We evaluate our methods though simulations and illustrate them in colorectal and pancreatic cancer data.
Keywords: Box-Cox; ROC; biomarker; cancer; censoring; classification; early detection; generalized gamma; kernels; limit of detection; spline.
Copyright © 2017 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures
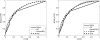
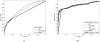
References
-
- Pepe MS, Etzioni R, Feng Z, Potter JD, Thompson ML, Thornquist M, Winget M, Yasui Y. Phases of Biomarker Development for Early Detection of Cancer. Journal of National Cancer Institute. 2001;93:1054–1061. - PubMed
-
- Taguchi A, Rho Jh, Yan Q, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Xu H, Tripathi SC, Wang H, Brenner DE, Kucherlapati M, Kucherlapati R, Boutin AT, Wang AY, DePinho RA, Feng Z, Lampe PD, Hanash SM. MAPRE1 as a Plasma Biomarker for Early-Stage Colorectal Cancer and Adenomas. Cancer Prevention Research. 2015 doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-15-0077. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- McLaughlin R, O'Hanlon D, Kerin M, Kenny P, Grimes H, Given HF. Are elevated Levels of the Tumour Marker CA19-9 of any clinical significance?-An evaluation. Clin Chem Lab Med. 1999;168(2):124–126. - PubMed
-
- Kim HR, Lee CH, Han SK, Shim YS, Yim JJ. Increased CA 19-9 level in patients without malignant disease. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2009;47:750–754. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
