Median preoptic glutamatergic neurons promote thermoregulatory heat loss and water consumption in mice
- PMID: 28786483
- PMCID: PMC5638873
- DOI: 10.1113/JP274667
Median preoptic glutamatergic neurons promote thermoregulatory heat loss and water consumption in mice
Abstract
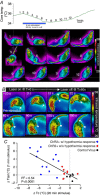
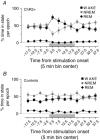
Key points: Glutamatergic neurons in the median preoptic area were stimulated using genetically targeted Channelrhodopsin 2 in transgenic mice. Stimulation of glutamatergic median preoptic area neurons produced a profound hypothermia due to cutaneous vasodilatation. Stimulation also produced drinking behaviour that was inhibited as water was ingested, suggesting pre-systemic feedback gating of drinking. Anatomical mapping of the stimulation sites showed that sites associated with hypothermia were more anteroventral than those associated with drinking, although there was substantial overlap.
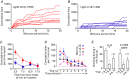
Abstract: The median preoptic nucleus (MnPO) serves an important role in the integration of water/electrolyte homeostasis and thermoregulation, but we have a limited understanding these functions at a cellular level. Using Cre-Lox genetic targeting of Channelrhodospin 2 in VGluT2 transgenic mice, we examined the effect of glutamatergic MnPO neuron stimulation in freely behaving mice while monitoring drinking behaviour and core temperature. Stimulation produced a strong hypothermic response in 62% (13/21) of mice (core temperature: -4.6 ± 0.5°C, P = 0.001 vs. controls) caused by cutaneous vasodilatation. Stimulating glutamatergic MnPO neurons also produced robust drinking behaviour in 82% (18/22) of mice. Mice that drank during stimulation consumed 912 ± 163 μl (n = 8) during a 20 min trial in the dark phase, but markedly less during the light phase (421 ± 83 μl, P = 0.0025). Also, drinking during stimulation was inhibited as water was ingested, suggesting pre-systemic feedback gating of drinking. Both hypothermia and drinking during stimulation occurred in 50% of mice tested. Anatomical mapping of the stimulation sites showed that sites associated with hypothermia were more anteroventral than those associated with drinking, although there was substantial overlap. Thus, activation of separate but overlapping populations of glutamatergic MnPO neurons produces effects on drinking and autonomic thermoregulatory mechanisms, providing a structural basis for their frequently being coordinated (e.g. during hyperthermia).
Keywords: autonomic nervous system; hypothalamus; hypothermia; optogenetic; sympathetic nervous system; temperature; thermoregulation; thirst.
© 2017 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2017 The Physiological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Baker MA, Doris PA & Hawkins MJ (1983). Effect of dehydration and hyperosmolality on thermoregulatory water losses in exercising dogs. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 244, R516–R521. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham JT, Beltz T, Johnson RF & Johnson AK (1992). The effects of ibotenate lesions of the median preoptic nucleus on experimentally‐induced and circadian drinking behavior in rats. Brain Res 580, 325–330. - PubMed
-
- Davern PJ & McKinley MJ (2013). Brain regions influenced by the lateral parabrachial nucleus in angiotensin II‐induced water intake. Neuroscience 252, 410–419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

