An Open-Label Pilot Study of Combined Augmentation With Creatine Monohydrate and 5-Hydroxytryptophan for Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor- or Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor-Resistant Depression in Adult Women
- PMID: 28787372
- PMCID: PMC5578880
- DOI: 10.1097/JCP.0000000000000754
An Open-Label Pilot Study of Combined Augmentation With Creatine Monohydrate and 5-Hydroxytryptophan for Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor- or Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor-Resistant Depression in Adult Women
Abstract
Purpose: Many women with major depressive disorder (MDD) respond inadequately to standard treatments. Augmentation of conventional antidepressants with creatine monohydrate and 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) could correct deficits in serotonin production and brain bioenergetics associated with depression in women, yielding synergistic benefit. We describe an open-label study of 5-HTP and creatine augmentation in women with MDD who had failed selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) monotherapy.
Methods: Fifteen women who were adequately adherent to an SSRI or SNRI and currently experiencing MDD, with a 17-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D) score of 16 or higher, were treated with 5 g of creatine monohydrate daily and 100 mg of 5-HTP twice daily for 8 weeks, with 4 weeks of posttreatment follow-up. The primary outcome was change in mean HAM-D scores.
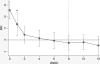
Results: Mean HAM-D scores declined from 18.9 (SD, 2.5) at pretreatment visits to 7.5 (SD, 4.4) (P < 0.00001), a decrease of 60%. Participants did not experience any serious treatment-related adverse events.
Conclusions: Combination treatment with creatine and 5-HTP may represent an effective augmentation strategy for women with SSRI- or SNRI-resistant depression. Given the limitations of this small, open-label trial, future study in randomized, placebo-controlled trials is warranted.
Figures


References
-
- Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler OJ, et al. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62:593–602. - PubMed
-
- Birnbaum HG, Kessler RC, Kelley D, et al. Employer burden of mild, moderate, and severe major depressive disorder: mental health services utilization and costs, and work performance. Depress Anxiety. 2010;27:78–89. - PubMed
-
- van der Voort TY, Seldenrijk A, van Meijel B, et al. Functional versus syndromal recovery in patients with major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76:809–814. - PubMed
-
- Kessler RC, Barber C, Birnbaum HG, et al. Depression in the workplace: effects on short-term disability. Health Aff (Millwood) 1999;18:163–171. - PubMed
-
- Bebbington PDG, Jenkins R, Lewis G, et al. The influence of age and sex on the prevalence of depressive conditions: report from the National Survey of Psychiatric Morbidity. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2003;15:74–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

