Epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation is involved in the induction of human hepatoma SMMC7721 cell proliferation by insufficient radiofrequency ablation
- PMID: 28789459
- PMCID: PMC5530000
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.6463
Epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation is involved in the induction of human hepatoma SMMC7721 cell proliferation by insufficient radiofrequency ablation
Abstract
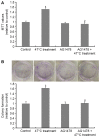
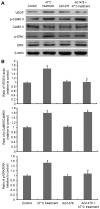
Our previous study revealed that insufficient radiofrequency ablation (RFA) promotes the malignancy of human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) SMMC7721 cells via the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)-induced overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). The aims of the present study were to address the involvement of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) transactivation in the enhanced SMMC7721 cell proliferation induced by insufficient RFA, in addition to its association with the CaMKII/ERK/VEGF signaling cascade. SMMC7721 cells were subjected to a 47°C treatment regimen to simulate insufficient RFA. Cell proliferation was determined using MTT and colony formation assays. The expression levels of VEGF, CaMKII, phosphorylated (phospho)-CaMKII, ERK, phospho-ERK, EGFR and phospho-EGFR were analyzed using western blotting. The results demonstrated that the enhancement of SMMC7721 cell proliferation by the 47°C treatment regimen was significantly inhibited by exposure of the cells to AG178 (a specific inhibitor of EGFR). Furthermore, AG1478 exposure prevented the overexpression of VEGF and phosphorylation of ERK, but had no significant effects on CaMKII phosphorylation. By contrast, 47°C treatment-induced EGFR phosphorylation was inhibited by treatment with KN93 (a specific inhibitor of CaMKII). Overall, the results of the present study have suggested a role for EGFR transactivation in the RFA-promoted growth of residual HCC. Thus, targeting EGFR may represent a useful preventive and therapeutic strategy for RFA-induced HCC progression and recurrence.
Keywords: Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; SMMC7721; epidermal growth factor receptor; proliferation; radiofrequency ablation.
Figures

References
-
- Che YH, Chongsuvivatwong V, Li L, Sriplung H, Wang YY, You J, Ma SJ, Yan Y, Zhang RY, Shen T, et al. Financial burden on the families of patients with hepatitis B virus-related liver diseases and the role of public health insurance in Yunnan province of China. Public Health. 2016;130:13–20. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2015.03.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang N, Wang L, Chai ZT, Zhu ZM, Zhu XD, Ma DN, Zhang QB, Zhao YM, Wang M, Ao JY, et al. Incomplete radiofrequency ablation enhances invasiveness and metastasis of residual cancer of hepatocellular carcinoma cell HCCLM3 via activating β-catenin signaling. PLoS One. 2014;9:e115949. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115949. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
