A High-Throughput Standard PCR-Based Genotyping Method for Determining Transgene Zygosity in Segregating Plant Populations
- PMID: 28791034
- PMCID: PMC5522864
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01252
A High-Throughput Standard PCR-Based Genotyping Method for Determining Transgene Zygosity in Segregating Plant Populations
Abstract
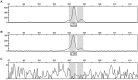
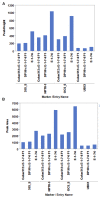
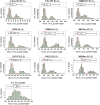
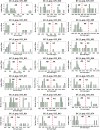
In crop research programs that implement transgene-based strategies for trait improvement it is necessary to distinguish between transgene homozygous and hemizygous individuals in segregating populations. Direct methods for determining transgene zygosity are technically challenging, expensive, and require specialized equipment. In this report, we describe a standard PCR-based protocol coupled with capillary electrophoresis that can identify transgene homozygous and hemizygous individuals in a segregating population without knowledge of transgene insertion site. PCR primers were designed to amplify conserved T-DNA segments of the 35S promoter, OCS terminator, and NPTII kanamycin resistance gene in the pHellsgate-8 RNAi construct for the Gossypium hirsutum phytochrome A1 gene. Using an optimized multiplexed reaction mixture and an amplification program of only 10 cycles we could discriminate between transgene homozygous and hemizygous cotton control DNA samples based on PCR product peak characteristics gathered by capillary electrophoresis. The protocol was refined by evaluating segregating transgenic progeny from nine BC1S1 populations derived from crosses between the transgenic cotton parent 'E-1-7-6' and other cotton cultivars. OCS PCR product peak height and peak area, normalized by amplification of the native cotton gene GhUBC1, revealed clear bimodal distributions of OCS product characteristics for each BC1S1 population indicating the presence of homozygous and hemizygous clusters which was further confirmed via K-means clustering. BC1S1 plants identified as homozygous or hemizygous were self-fertilized to produce BC1S2 progeny. For the homozygous class, 19/20 BC1S2 families confirmed the homozygous BC1S1 prediction while 21/21 BC1S2 families confirmed the hemizygous prediction of the original parent. This relatively simple protocol provides a reliable, rapid, and high-throughput way of evaluating segregating transgenic populations using methods and equipment common to crop molecular breeding labs.
Keywords: PCR; bimodal; cotton; method; plant breeding; transgene.
Figures

References
-
- Hartigan J. A. (1985). Statistical theory in clustering. J. Classif. 2 63–76. 10.1007/BF01908064 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

