Down-Regulation of TGF-β Expression Sensitizes the Resistance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells to Sorafenib
- PMID: 28792132
- PMCID: PMC5552643
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.5.899
Down-Regulation of TGF-β Expression Sensitizes the Resistance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells to Sorafenib
Abstract
Purpose: Sorafenib, a multikinase inhibitor, is the standard therapy for patients with advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, resistance develops to the treatment, therefore, we tried to unravel the underlying mechanism in the resistance of HCC cells to sorafenib via the development of more effective therapeutic strategies.
Materials and methods: Various liver cancer cell lines were treated with either sorafenib only or with sorafenib after infection of adenovirus expressing short hairpin RNA (shRNA) against transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and p38 activity was examined using western blotting.
Results: p38 MAP kinase activity was inhibited by low concentrations of sorafenib, which could potentially lead to sorafenib resistance in HCC cell lines. Subsequently, we used constitutive form of MKK3/6 (MKK3/6E) to confirm that massive cell death was induced by the activation of p38, and demonstrated the ability to activate p38 without any stimulation. In addition, sorafenib resistance was reduced by the activation of p38. Subsequently, we confirmed that TGF-β shRNA effectively recovered the phosphorylation of p38 inhibited by sorafenib, and increased the sensitivity of HCC cells to sorafenib, thereby inducing cell death and overcoming the resistance of HCC cells to sorafenib.
Conclusion: Our study provides a new therapeutic strategy for HCC that overcomes the resistance of HCC to sorafenib by down-regulation of TGF-β.
Keywords: HCC; TGF-β; adenovirus; p38; resistance; sorafenib.
© Copyright: Yonsei University College of Medicine 2017
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
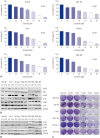
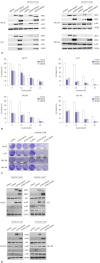

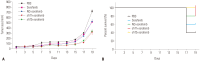
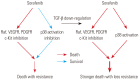
References
-
- Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2003;362:1907–1917. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:378–390. - PubMed
-
- Bruix J, Sherman M Practice Guidelines Committee, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2005;42:1208–1236. - PubMed
-
- Zhai B, Hu F, Jiang X, Xu J, Zhao D, Liu B, et al. Inhibition of Akt reverses the acquired resistance to sorafenib by switching protective autophagy to autophagic cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13:1589–1598. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

