pH-sensitive pHLIP® coated niosomes
- PMID: 28792261
- PMCID: PMC5658010
- DOI: 10.1080/09687688.2017.1342969
pH-sensitive pHLIP® coated niosomes
Abstract
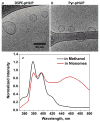
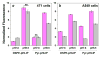
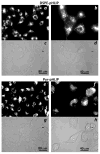
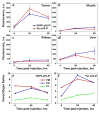
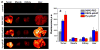
Nanomedicine is becoming very popular over conventional methods due to the ability to tune physico-chemical properties of nano vectors, which are used for encapsulation of therapeutic and diagnostic agents. However, the success of nanomedicine primarily relies on how specifically and efficiently nanocarriers can target pathological sites to minimize undesirable side effects and enhance therapeutic efficacy. Here, we introduce a novel class of targeted nano drug delivery system, which can be used as an effective nano-theranostic for cancer. We formulated pH-sensitive niosomes (80-90 nm in diameter) using nonionic surfactants Span20 (43-45 mol%), cholesterol (50 mol%) and 5 mol% of pH (Low) insertion peptide (pHLIP) conjugated with DSPE lipids (DSPE-pHLIP) or hydrophobic fluorescent dye, pyrene, (Pyr-pHLIP). In coating of niosomes, pHLIP was used as an acidity sensitive targeting moiety. We have demonstrated that pHLIP coated niosomes sense the extracellular acidity of cancerous cells. Intravenous injection of fluorescently labeled (R18) pHLIP-coated niosomes into mice bearing tumors showed significant accumulation in tumors with minimal targeting of kidney, liver and muscles. Tumor-targeting niosomes coated with pHLIP exhibited 2-3 times higher tumor uptake compared to the non-targeted niosomes coated with PEG polymer. Long circulation time and uniform bio-distribution throughout the entire tumor make pHLIP-coated niosomes to be an attractive novel delivery system.
Keywords: Drug delivery; fluorescence imaging; targeting tumor acidity.
Conflict of interest statement
OA Andreev and YK Reshetnyak have founded and have a financial interest in a company, pHLIP, Inc., with the aim of bringing pHLIP technology to the clinic. The company has had no involvement in funding the studies reported here.
Figures

References
-
- AMMAR H, GHORAB M, EL-NAHHAS S, HIGAZY I. Proniosomes as a carrier system for transdermal delivery of tenoxicam. International journal of pharmaceutics. 2011;405:142–152. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
