Trigeminovascular calcitonin gene-related peptide function in Cacna1a R192Q-mutated knock-in mice
- PMID: 28792272
- PMCID: PMC6446415
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X17725673
Trigeminovascular calcitonin gene-related peptide function in Cacna1a R192Q-mutated knock-in mice
Abstract
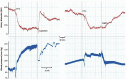
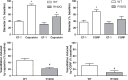
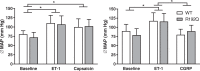
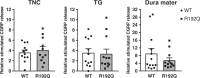
Familial hemiplegic migraine type 1 (FHM1) is a rare migraine subtype. Whereas transgenic knock-in mice with the human pathogenic FHM1 R192Q missense mutation in the Cacna1a gene reveal overall neuronal hyperexcitability, the effects on the trigeminovascular system and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor are largely unknown. This gains relevance as blockade of CGRP and its receptor are therapeutic targets under development. Hence, we set out to test these effects in FHM1 mice. We characterized the trigeminovascular system of wild-type and FHM1 mice through: (i) in vivo capsaicin- and CGRP-induced dural vasodilation in a closed-cranial window; (ii) ex vivo KCl-induced CGRP release from isolated dura mater, trigeminal ganglion and trigeminal nucleus caudalis; and (iii) peripheral vascular function in vitro . In mutant mice, dural vasodilatory responses were significantly decreased compared to controls. The ex vivo release of CGRP was not different in the components of the trigeminovascular system between genotypes; however, sumatriptan diminished the release in the trigeminal ganglion, trigeminal nucleus caudalis and dura mater but only in wild-type mice. Peripheral vascular function was similar between genotypes. These data suggest that the R192Q mutation might be associated with trigeminovascular CGRP receptor desensitization. Novel antimigraine drugs should be able to revert this complex phenomenon.
Keywords: Calcitonin gene-related peptide; R192Q; migraine; trigeminovascular; vasodilation.
Figures
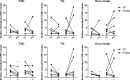
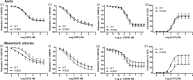
References
-
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society. The international classification of headache disorders, 3 rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia 2013; 33: 629–808. - PubMed
-
- Lauritzen M. Pathophysiology of the migraine aura. The spreading depression theory. Brain 1994; 117(Pt 1): 199–210. - PubMed
-
- Karsan N, Goadsby PJ. Calcitonin gene-related peptide and migraine. Curr Opin Neurol 2015; 28: 250–254. - PubMed
-
- Ferrari MD, Klever RR, Terwindt GM, et al. Migraine pathophysiology: lessons from mouse models and human genetics. Lancet Neurol 2015; 14: 65–80. - PubMed
-
- Ophoff RA, Terwindt GM, Vergouwe MN, et al. Familial hemiplegic migraine and episodic ataxia type-2 are caused by mutations in the Ca2+ channel gene CACNL1A4. Cell 1996; 87: 543–552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

