Global, Regional, and National Prevalence, Incidence, and Disability-Adjusted Life Years for Oral Conditions for 195 Countries, 1990-2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors
- PMID: 28792274
- PMCID: PMC5912207
- DOI: 10.1177/0022034517693566
Global, Regional, and National Prevalence, Incidence, and Disability-Adjusted Life Years for Oral Conditions for 195 Countries, 1990-2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors
Abstract
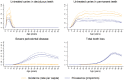
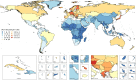
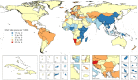
The Global Burden of Disease 2015 study aims to use all available data of sufficient quality to generate reliable and valid prevalence, incidence, and disability-adjusted life year (DALY) estimates of oral conditions for the period of 1990 to 2015. Since death as a direct result of oral diseases is rare, DALY estimates were based on years lived with disability, which are estimated only on those persons with unmet need for dental care. We used our data to assess progress toward the Federation Dental International, World Health Organization, and International Association for Dental Research's oral health goals of reducing the level of oral diseases and minimizing their impact by 2020. Oral health has not improved in the last 25 y, and oral conditions remained a major public health challenge all over the world in 2015. Due to demographic changes, including population growth and aging, the cumulative burden of oral conditions dramatically increased between 1990 and 2015. The number of people with untreated oral conditions rose from 2.5 billion in 1990 to 3.5 billion in 2015, with a 64% increase in DALYs due to oral conditions throughout the world. Clearly, oral diseases are highly prevalent in the globe, posing a very serious public health challenge to policy makers. Greater efforts and potentially different approaches are needed if the oral health goal of reducing the level of oral diseases and minimizing their impact is to be achieved by 2020. Despite some challenges with current measurement methodologies for oral diseases, measurable specific oral health goals should be developed to advance global public health.
Keywords: caries; dental public health; epidemiology; global health; periodontal diseases; tooth loss.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Comment in
-
The Global Burden of Oral Disease: Research and Public Health Significance.J Dent Res. 2017 Apr;96(4):361-363. doi: 10.1177/0022034517693567. Epub 2017 Feb 1. J Dent Res. 2017. PMID: 28318392 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bergström J. 2014. Smoking rate and periodontal disease prevalence: 40-year trends in Sweden 1970–2010. J Clin Periodontol. 41(10):952–957. - PubMed
-
- Broadbent JM, Foster Page LA, Thomson WM, Poulton R. 2013. Permanent dentition caries through the first half of life. Br Dent J. 215(7):E12. - PubMed
-
- Dye BA, Tan S, Smith V, Lewis BG, Barker LK, Thornton-Evans G, Eke PI, Beltrán-Aguilar ED, Horowitz AM, Li CH. 2007. Trends in oral health status: United States, 1988–1994 and 1999–2004. Vital Health Stat. 11(248):1–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

